Instrukcja obsługi Lightware HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-FOX
Lightware
przedłużacz AV
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-FOX
Przeczytaj poniżej 📖 instrukcję obsługi w języku polskim dla Lightware HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-FOX (73 stron) w kategorii przedłużacz AV. Ta instrukcja była pomocna dla 7 osób i została oceniona przez 2 użytkowników na średnio 4.5 gwiazdek
Strona 1/73

HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
User’s Manual
Multimode Single Fiber Optical Extender

HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 2
Important Safety Instructions
Class I apparatus construction
This equipment must be used with a mains power system with a
protective earth connection. The third (earth) pin is a safety feature,
do not bypass or disable it. The equipment should be operated only
from the power source indicated on the product.
To disconnect the equipment safely from power, remove the power
cord from the rear of the equipment, or from the power source. The
MAINS plug is used as the disconnect device, the disconnect device
shall remain readily operable.
There are no user-serviceable parts inside of the unit. Removal of the
cover will expose dangerous voltages. To avoid personal injury, do not
remove the cover. Do not operate the unit without the cover installed.
The appliance must be safely connected to multimedia systems.
Follow instructions described in this manual.
Ventilation
For the correct ventilation and to avoid overheating ensure enough
free space around the appliance. Do not cover the appliance, let the
ventilation holes free and never block or bypass the ventilators (if any).
WARNING
To prevent injury, the apparatus is recommended to securely attach to
the oor/wall or mount in accordance with the installation instructions.
The apparatus shall not be exposed to dripping or splashing and that
no objects lled with liquids, such as vases, shall be placed on the
apparatus. No naked ame sources, such as lighted candles, should
be placed on the apparatus.
CAUTION AVIS
RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK
DO NOT OPEN
RISQUE DE CHOC ELECTRIQUE
NE PAS OUVRIR
Waste Electrical & Electronic Equipment
WEEE
This marking shown on the product or its literature,
indicates that it should not be disposed with other
household wastes at the end of its working life. To
prevent possible harm to the environment or human
health from uncontrolled waste disposal, please
separate this from other types of wastes and recycle it
responsibly to promote the sustainable reuse of material
resources. Household users should contact either the
retailer where they purchased this product, or their local government
ofce, for details of where and how they can take this item for
environmentally safe recycling. Business users should contact their
supplier and check the terms and conditions of the purchase contract.
This product should not be mixed with other commercial wastes for
disposal.
Caution: Laser product
INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION
AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
CLASS 3R LASER PRODUCT
Radiated wavelengths:
778 nm, 801 nm, 824 nm, 850 nm, 911 nm
Output power <= 1 mW
Classified by EN 60825-1:2008
Common Safety Symbols
Symbol Description
Alternating current
Protective conductor terminal
Caution, possibility of eletric shock
Caution
Laser radiation

HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 3
Symbol Legend
The following symbols and markings are used in the document:
WARNING! Safety-related information which is highly
recommended to read and keep in every case!
ATTENTION! Useful information to perform a successful procedure;
it is recommended to read.
INFO: A notice which contains additional information. Procedure
can be successful without reading it.
DEFINITION: The short description of a feature or a function.
TIPS AND TRICKS: Ideas which you may have not known yet but can
be useful.
Navigation Buttons
Go back to the previous page. If you clicked on a link previously,
you can go back to the source page by clicking the button.
Navigate to the Table of Contents.
Step back one page.
Step forward to the next page.
Document Information
All presented functions refer to the indicated products. The descriptions
have been made during testing these functions in accordance with the
indicated Hardware/Firmware/Software environment:
Item Version
Lightware Device Controller (LDC) software 1.21.0
Lightware Device Updater Software 1.5.2
Controller rmware 1.1.0
Hardware 1.2
Document revision: 1.1
Release date: 28-02-2018
Editor: Judit Barsony

HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 4
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION 6 ...................................................................................
1.1. Description ...................................................................................6
1.2. Model Denomination ....................................................................6
1.3. Box Contents ...............................................................................6
1.4. Compatible Devices ......................................................................6
1.5. Features of the Device .................................................................6
1.6. Typical Application .....................................................................7
1.6.1. Integrated System Application ........................................................ 7
1.6.2. Standalone Application .................................................................... 8
2. INSTALLATION 9 .....................................................................................
2.1. Mounting Options ........................................................................9
2.1.1. Truss Mounting - HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro .................................. 9
2.1.2. Standard Rack Installation .............................................................. 9
2.1.3. Rack Shelf Mounting (with 1U high Rack Shelf) ........................... 10
2.2. Connecting Steps ....................................................................... 11
3. PRODUCT OVERVIEW 12 ......................................................................
3.1. Front View ..................................................................................12
3.2. Rear View ....................................................................................13
3.3. Electrical Connections .............................................................13
3.4. Multimode Single Fiber Extender Concept ................................ 14
3.4.1. Summary of Interfaces - Transmitter ............................................ 14
3.4.2. Summary of Interfaces - Receiver ................................................. 14
3.5. Optical Interface ....................................................................... 15
3.6. Video and Audio Interface .......................................................... 16
3.6.1. Output Conversion Modes ............................................................. 16
3.6.2. Autoselect Feature ......................................................................... 16
3.7. Control Features ......................................................................17
3.7.1. USB Control Interface ..................................................................... 17
3.7.2. Ethernet Interface ........................................................................... 17
3.7.3. Serial Interface ................................................................................ 18
4. OPERATION 19 .......................................................................................
4.1. Powering on ...............................................................................19
4.2. Front Panel Operations ............................................................19
4.2.1. Function Button - HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro ................................ 20
4.2.2. Boot Button ..................................................................................... 20
4.2.3. Function Button - HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro ................................ 20
4.2.4. Boot Button ..................................................................................... 20
4.3. Front Panel LCD Menu Operations ............................................ 21
4.3.1. System Settings Menu ................................................................... 21
4.3.2. Ports Menu ..................................................................................... 22
4.3.3. EDID Menu ..................................................................................... 22
4.3.4. Health Menu .................................................................................... 23
4.3.5. Remote Menu ................................................................................. 23
5. SOFTWARE CONTROL – LIGHTWARE DEVICE CONTROLLER 24 ...
5.1. Install and Upgrade ..................................................................24
5.2. Establishing the Connection ..................................................... 24
5.3. Crosspoint Menu - HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro...........................25
5.4. Port Properties Window ...........................................................26
5.4.1. HDMI Input Port -Transmitter ........................................................ 26
5.4.2. HDMI Output Port - Transmitter ..................................................... 26
5.4.3. Optical Input Port - Receiver .......................................................... 27
5.4.4. HDMI Output Port - Receiver .......................................................... 27
5.5. EDID Menu ...................................................................................28
5.5.1. Sources and Destinations .............................................................. 28
5.5.2. EDID Operations.............................................................................. 28
5.5.3. EDID Summary Window ................................................................. 29
5.5.4. Editing an EDID ............................................................................... 29
5.5.5. Creating an EDID ............................................................................. 30
5.6. Control Menu ............................................................................30
5.6.1. RS-232 Tab ...................................................................................... 30
5.6.2. Ethernet Tab ................................................................................... 31
5.7. Event Manager ...........................................................................31
5.7.1. The Event Editor .............................................................................. 32
5.7.2. Create or Modify an Event .............................................................. 32
5.7.3. Special Tools and Accessories ...................................................... 34
5.7.4. Clear One or More Event(s) ............................................................ 34
5.7.5. Export and Import Events .............................................................. 34
5.8. Settings Menu ............................................................................35
5.8.1. Status Tab ....................................................................................... 35
5.8.2. Network Tab .................................................................................... 35
5.8.3. Front Panel Tab ............................................................................... 35
5.8.4. Backup Tab (Configuration Cloning) ............................................. 36
5.8.5. System ............................................................................................ 37
5.9. Advanced View Window ..............................................................37
6. LW3 PROGRAMMERS’ REFERENCE 38 ...............................................
6.1. Overview .....................................................................................38
6.1.1. Elements of the Tree Structure ...................................................... 38
6.1.2. Escaping .......................................................................................... 40
6.1.3. Error Messages ............................................................................... 40
6.1.4. Prefix Summary .............................................................................. 40
6.2. The Tree Structure .................................................................... 40
6.3. LW3 Commands ...........................................................................41
6.3.1. Get Command ................................................................................. 41
6.3.2. Set Command ................................................................................. 42
6.3.3. Invocation ....................................................................................... 42
6.3.4. Manual ............................................................................................ 43
6.3.5. Signature ......................................................................................... 43
6.3.6. Subscription .................................................................................... 43
6.3.7. Notifications about the Changes of the Properties ..................... 44
6.4. Formal Definitions .....................................................................44
6.5. System Commands ...................................................................... 45
6.5.1. Querying the Product Name .......................................................... 45
6.5.2. Setting the Device Label ................................................................. 45
6.5.3. Querying the Serial Number ........................................................... 45
6.5.4. Querying the Firmware Version ..................................................... 45
6.5.5. Resetting the Extender ................................................................... 45
6.5.6. Restoring the Factory Default Settings ......................................... 45
6.5.7. Locking Front Panel ........................................................................ 45
6.5.8. Enabling Dark Mode ....................................................................... 45
6.5.9. Setting the Dark Mode Delay ......................................................... 46
6.5.10. Setting the Dark Mode on the Remote Device ............................ 46
6.5.11. Setting the Rotary Direction of the Jog Dial Knob ...................... 46
6.6. Video Port and Crosspoint Settings ......................................... 46
6.6.1. Querying the Crosspoint Setting .................................................... 46
6.6.2. Switching Video Input .................................................................... 46
6.6.3. Querying the Status of Source Ports ............................................. 47
6.6.4. Querying the Status of Destination Ports ..................................... 48
6.6.5. Muting Input Port ............................................................................ 48
6.6.6. Unmuting Input Port ....................................................................... 48
6.6.7. Locking Input Port .......................................................................... 48
6.6.8. Unlocking Input Port ....................................................................... 48
6.6.9. Querying the Video Autoselect Settings ....................................... 48
6.6.10. Changing the Autoselect Mode ................................................... 49
6.6.11. HDCP Setting ................................................................................ 49
6.6.12. Setting the Output Conversion Mode .......................................... 49
6.6.13. Setting the Output Conversion Mode of the Remote Device ..... 49

HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 5
6.7. Network Configuration .............................................................50
6.7.1. Querying the IP Address................................................................. 50
6.7.2. Changing the IP Address (Static) .................................................. 50
6.7.3. Querying the Subnet Mask ............................................................. 50
6.7.4. Changing the Subnet Mask (Static) .............................................. 50
6.7.5. Querying the Gateway Address ..................................................... 50
6.7.6. Changing the Gateway Address (Static) ....................................... 50
6.7.7. Querying the DHCP State ............................................................... 50
6.7.8. Changing the DHCP State .............................................................. 50
6.7.9. Enabling Ethernet Port ................................................................... 50
6.8. RS-232 Port Configuration .......................................................51
6.8.1. Querying the RS-232 Opearation Mode ......................................... 51
6.8.2. Setting the RS-232 Opearation Mode ............................................ 51
6.8.3. Setting the BAUD Rate .................................................................... 51
6.8.4. Setting the Databit .......................................................................... 51
6.8.5. Setting the Stopbits ........................................................................ 51
6.8.6. Setting the Parity ............................................................................ 51
6.8.7. Enabling Command Injection Mode ............................................. 52
6.9. Sending Message via the Communication Ports .......................52
6.9.1. Sending Message via an RS-232 Port ........................................... 52
6.9.2. Sending Message via TCP Port ..................................................... 52
6.9.3. Sending Message via UDP Port ..................................................... 53
6.10. EDID Management ..................................................................... 54
6.10.1. Querying the Emulated EDIDs ...................................................... 54
6.10.2. Querying the Validity of a Dynamic EDID .................................... 54
6.10.3. Querying the Preferred Resolution of an User EDID ................... 54
6.10.4. Emulating an EDID to an Input Port ............................................. 54
6.10.5. Copying an EDID to User Memory ............................................... 54
6.10.6. Deleting an EDID from User Memory .......................................... 54
6.10.7. Resetting the Emulated EDIDs ..................................................... 54
6.11. LW3 Commands - Quick Summary .............................................55
7. FIRMWARE UPGRADE 57 ......................................................................
7.1. About the Firmware Package (LFP File).....................................57
7.2. Short Instructions .................................................................... 57
7.3. Install and Upgrade ..................................................................57
7.4. Detailed Instructions ................................................................58
7.4.1. Establish the Connection ............................................................... 58
7.4.2. Start the LDU and Follow the Instructions .................................... 58
7.5. Keeping the Configuration Settings .........................................61
8. TROUBLESHOOTING 62 ........................................................................
9. TECHNOLOGIES 64 ................................................................................
9.1. EDID Management ....................................................................... 64
9.1.1. Understanding the EDID ................................................................. 64
9.1.2. Advanced EDID Management ........................................................ 64
9.2. HDCP Management .....................................................................65
9.2.1. Protected and Unprotected Content ............................................. 65
9.2.2. Disable Unnecessary Encryption ................................................... 65
9.3. Pixel Accurate Reclocking .......................................................66
9.4. Serial Management ....................................................................67
9.4.1. General Information ....................................................................... 67
9.4.2. Types of Serial Cables .................................................................... 67
9.4.3. RS-232 Signal Transmission over Lightware Extender Devices .. 67
10. APPENDIX ........................................................................................68
10.1. Specification ............................................................................68
10.2. Content of Backup File ............................................................69
10.3. Factory Default Settings .......................................................69
10.4. Maximum Extension Distances .................................................70
10.5. Factory EDID List .....................................................................71
10.6. Mechanical Drawings ..............................................................72
10.6.1. HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro ........................................................... 72
10.6.2. HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro ........................................................... 72
10.7. Further Information ................................................................ 73
1. Introduction HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 6
1
Introduction
Thank You for choosing Lightware’s HDMI20-OPTC series device. In the rst
chapter we would like to introduce the device highlighting the most important
features in the below listed sections:
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
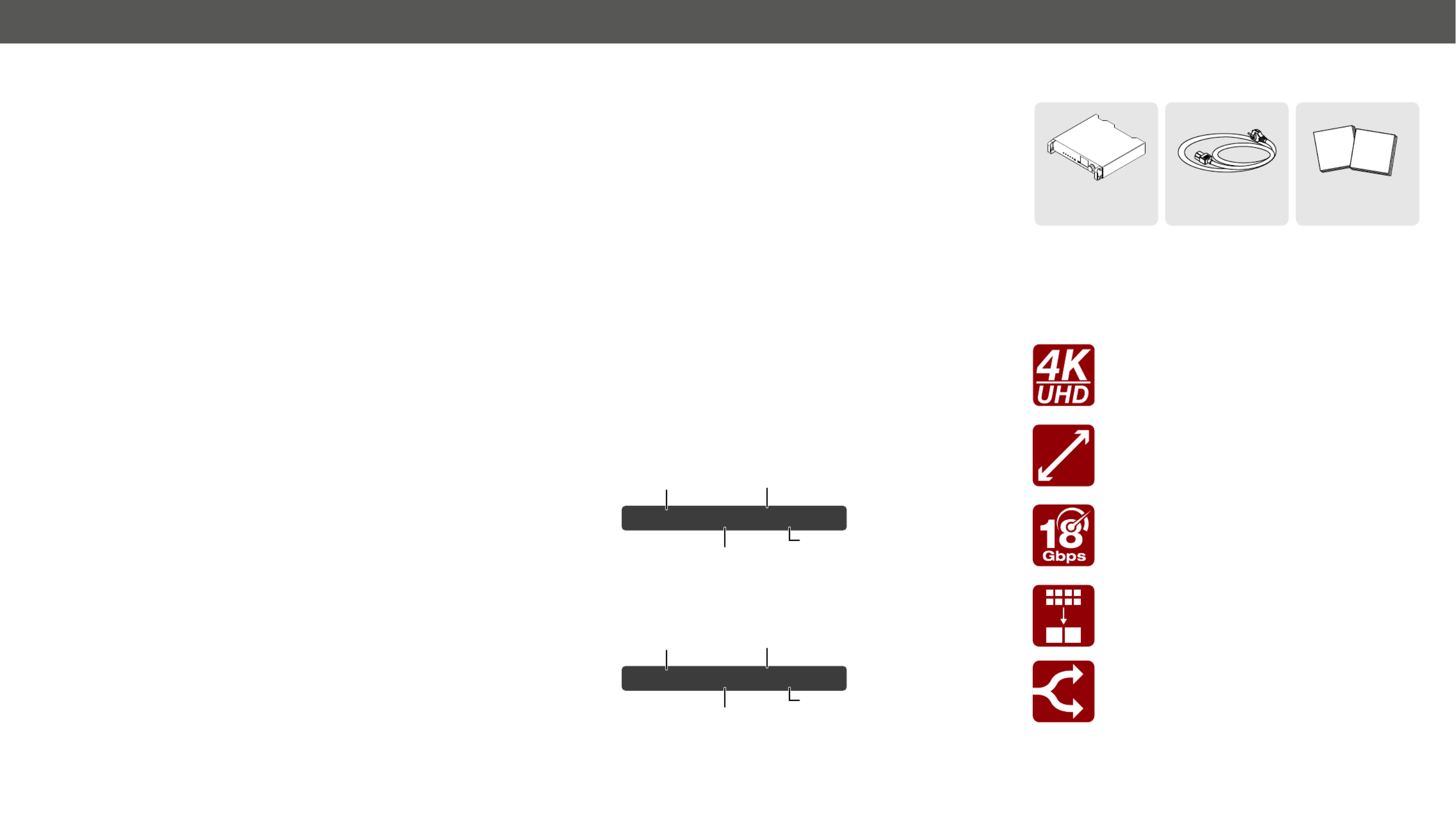
1.3. Box Contents
1.4. Compatible Devices
HDMI20-OPTC series devices are compatible with each other.
For more information, please check the compatibility table on
www.lightware.com.
1.5. Features of the Device
4K Video without Compression
Supporting uncompressed 4K UHD resolution at 60Hz
4:4:4 colorspace.
700m
4K UHD
@60Hz
Signal Transmission up to 700m
18 Gbit/sec Bandwidth
The extender can transmit HDMI 2.0 signals with
18Gbps.
Conversion to 4:2:0
The receiver is able to subsample the video stream in
YCbCr colorspace from 4:4:4 to 4:2:0.
HDMI 2.0 to 2x HDMI 1.4 Splitting
The device supports left and right column processing
of an HDMI 2.0 4K@60Hz 4:4:4 input signal, allowing
for the transmission of an 18 Gbps HDMI 2.0 signal
over two HDMI 1.4 compliant links. The two halves can
then be recombined at the signal destination.
receiver unit
IEC power connector Safety & warranty info,
Safety and
Warranty
Info
Quick
Start
Guide
1.1. Description
Thank You for choosing Lightware HDMI20-OPTC series products.
a HDMI 2.0 compatible extender pair for video, RS-232 and Gigabit
Ethernet signals, supporting uncompressed 4K UHD resolution at
60Hz 4:4:4. This extender pair is particularly recommended for rental
and staging applications, 4K live events, and for future-proof operation
centers. The extender can transmit HDMI 2.0 signals with 18Gbps
Using the factory, custom or transparent EDID emulation the user
Management forces the required resolution from any video source
The unit offers bi-directional and transparent RS-232 transmission
All devices can be mounted on a rack shelf or used standalone, rack
ears also serve easy handling and bump protection, mounting threads
on top and one of the sides to conform strict installation safety
regulations.
1.2. Model Denomination
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 capable
Lightware optical standard
Transmitter unit
Model number
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 capable
Lightware optical standard
Receiver unit
Model number

1. Introduction HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 7
TX
RX
Local Output
User can attach a local monitor to observe the video
signal sent through the ber optical cable. The
resolution and clock frequency are the same on HDMI
and ber optical connectors, no internal scaling or
conversion is applied.
Graphic Display and Rotary Jog Dial Control Knob
Easy setting and menu navigation are assured by the
color graphic display and the comfortable jog dial
control.
Event Manager
The Event Manager tool takes care of all the necessary
control in a smaller conguration by performing
predened actions in response to device status
changes. Hence, in a less complex environment, there
is no need to invest in additional control solutions,
which makes the receiver the best choice for numerous
applications.
Dark Mode
Rental application requires this function, which keeps
the LEDs unlit to hide the device during the event.
Mounting Threads
Mounting threads on top and one of the sides to
conform strict installation safety regulations.
1.6. Typical Application
▪Rental and staging
▪Long distance lossless HDMI or DVI signal transmission
▪Professional AV systems, conference rooms
1.6.1. Integrated System Application
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI20-O PTC-TX2 20-Pro
MX2-8x8-HDMI20-Audio
MX-RCP16
4K monitor
4K monitor
Xbox WiFi Router
Projector
4K PC
MacBook Pro
TX
HDMI20
OPTC
PO
WER /
LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SEL
ECT
USB
CONTROL
HDM
I20-
OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2
.0 Multimo
de Fibe
r Transmi tter
LIVE
POWER
IR
RES
ET
MX
2-8x8-HDMI20-Audio
Compact HDMI 2.0 M atrix Switcher
DEST
INATIONS
TX
RX
HD MI20
OPTC
POWER
/ LIVE
FIBE
R LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INP
UT2
SEL
ECT
USB
CONT
ROL
HDM
I20-
OPTC
-R
X2
20-Pr
o
HDM
I 2.0
Multim o de Fiber Rec
eiver
RX
HDMI
CATx (LAN)
Optical fiber
Display Port
1. Introduction HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 8
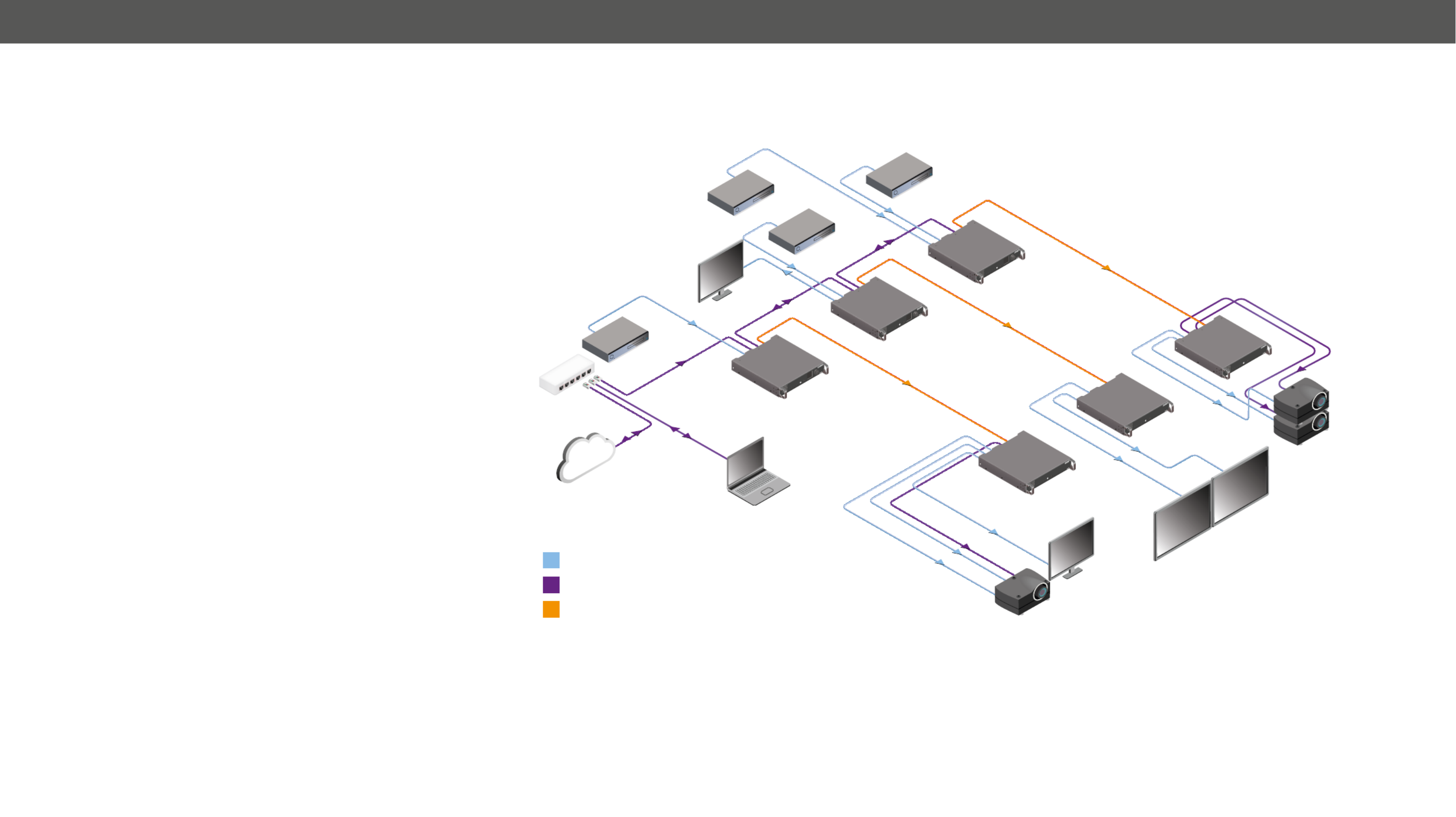
1.6.2. Standalone Application
Typical Application Description
The two Ethernet connectors on each extender make possible to daisy
chain the devices and build a local network where all the transmitters
(1..3) and receivers (1..3) are available via LAN.
They can be controlled by Lightware Device Controller (LDC) software
from the laptop. Optical ber cable transmits the HDMI, embedded
audio, Ethernet, and RS-232 signal to the receivers, so in this case,
the sinks can be controlled by Ethernet commands from the control
device (laptop).
In this example, all the sources send HDMI 2.0 4K@60Hz 4:4:4 A/V
signal to the transmitters which extend the stream to the receivers via
multimode ber cable.
Receiver 1..3 represent three applications of the output modes:
▪RX1 is in transparent mode (no conversion mode), the sinks are
stacked projectors. The video signal is HDMI 2.0 4K@60Hz
4:4:4 on the Output 1A and the Output 2 ports.
▪RX2 is in downsample convert mode (convert to YCbCr 4:2:0). The
LED screen 2 is 4K compatible and connected to the Output 2
port. LED screen 1 is not HDMI 2.0 4K@60Hz 4:4:4 compliant, so
the video processor in the receiver converts the HDMI signal from
4:4:4 to 4:2:0, and this way the sink will be able to accept the signal
on the Output 1B.
▪RX3 is in split mode. The receiver supports vertical splitting of
the HDMI 2.0 4K@60Hz 4:4:4 input signal to left and right halves
allowing for the transmission of a 18Gbps HDMI 2.0 signal over
two HDMI1.4 compliant links. The sink is a projector which is
able to recombine two half signals. Video signal is transmitted
to the Output 2 without any changing.
HDMI
LAN
Optical fiber
TX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Trans mitter
TX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Trans mitter
TX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Trans mitter
RX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiv er
RX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiv er
RX
HDMI20
OPTC
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT1
INPUT2
SELECT
USB
CONTROL
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiv er
RX1
RX2
RX3
TX1
TX2
Media
player 1
Media
player 3
Media
player 2
Local
LCD
LCD
monitor
LED screen
1
LED screen
2
Media
player 4
Projector
3
Laptop
LDC Control TX 1-3
LDC Control RX 1-3
Control Projector 1-3
Up to 700 m
OUTPUT 1A (18G)
OUTPUT 2 (18G 4:4:4)
OUTPUT 1B (9G 4:2:0)
OUTPUT 2 (18G)
OUTPUT 1A (1×9G L/R)
OUTPUT 1B (1×9G L/R)
OUTPUT 2 (18G)
Up to 700 m
Up to 700 m
Projector
1
Projector
2
TX3
Media
player 2
INT ERNET
Ethernet switch

2. Installation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 9
2.1.2. Standard Rack Installation
Rack mounting kit includes all necessary accessories for
Standard Rack Installation:
▪2 pcs. rack ears,
▪12 pcs. black, M4x8mm hexagon socket countersunk head
screws.
Rack mounting kit is not supplied with the product, it can be purchased
separately, please contact sales@lightware.com.
Step 1. Take two devices directly each other.
Step 2. Two mounting holes on the front ears and two on the back of
the chassis is for fastening the two units to each other with 2x
2 pcs. M4x8 mm screws. This way you get a one-rack wide and
1U high device.
Transmitter 1.
Front side
Back side
Transmitter 2.
Transmitter 1.
Front rack ears
Transmitter 2.
M4x8 mm
screw
Front side
M4x6 mm screw
nut screw
M4x6 mm
screw
nut screw
M4x6 mm
screw
nut screw
M4x6 mm
screw
nut screw
M4x6 mm
screw
nut screw
Transmitter 2. Transmitter 1.
Back side
M4x8 mm
screw
M4x8 mm
screw
M4x8 mm
screw
2
Installation
The chapter is about the installation of the device and connecting to other
appliances, presenting also the mounting options and further assembly steps:
ÝMounting Options
ÝConnecting Steps
2.1. Mounting Options
Extenders can be mounted in several ways, depending on the
application. They can be mounted on a rack shelf or used standalone.
Rack ears also serve easy handling and bump protection, mounting
threads on top and one of the sides to conform strict installation
safety regulations.
ATTENTION! To ensure the correct ventilation and avoid overheating
let enough free space in front of the appliance and keep the
ventilation holes free.
2.1.1. Truss Mounting - HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
Mounting thread on top and on one of the sides for safe and secure
installation. Rigging the handles with a safety wire rope is highly
recommended for safety reasons.
To order mounting accessories please contact sales@lightware.com.
(Truss clamp and safety wire rope are not available at sales.)
M10x16mm
screw
M10x16mm
screw

2. Installation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 10
ATTENTION! Take care of the mounting direction of the screws!
Mounting direction of the screws
Step 3. Take the rack ears on the left and right side of the extender pair
as shown in the picture. Insert the screws into the holes and x
the front ears to the devices.
Assembly of the mounting ears
Front side
Tx 1.
Threaded hole
on this side
Screw from
the right
Screw from
the left Threaded hole
on this side
Tx 2.
Back side
Tx 2.
Threaded hole
on this side
Screw from
the right
Screw from
the left Threaded hole
on this side
Tx 1.
Transmitter 1.
Transmitter 2.
Step 4. As a nal step, mount the unit in the rack.
Standard rack installation
ATTENTION! Always use all the four screws for xing the rack ears
to the rack rail. Choose properly sized screws for mounting. Keep
minimum two thread left after the nut screw.
Mounting the rack ears to the rack rail
min. 2
thread left
rack rail
rack shelf mounting ear
rack screw
flat washer
cage nut
2.1.3. Rack Shelf Mounting (with 1U high Rack Shelf)
1U high rack shelf provides mounting holes for fastening two 1/2-rack
or four 1/4-rack size units. Supplied accessories:
▪10 pcs. PZ at head screw (M3x6mm).
Rack shelf is not supplied with the product, it can be purchased
separately, please contact . sales@lightware.com
Step 1. Turn the unit upside down.
Step 2. Put the rack shelf upside down on the unit, and position it to get
the mounting holes aligned.
Step 3. Fasten the unit on the rack shelf with the provided screws.
Step 4. Mount the rack shelf in the rack.
INFO: The extender is half-rack sized.

2. Installation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 11
2.2. Connecting Steps
OPT
Connect a multimode (MM) ber cable to the channel A of the transmitter.
OPT
Optionally connect a compatible Lightware device or a third-party device to the break-out LC
connector. It is internally linked to the channel B of the Neutrik connector.
HDMI
Connect an HDMI source (e.g. video processor or media server) to any of the inputs of the
transmitter.
HDMI
Optionally connect an HDMI sink (e.g. condence monitor) to the HDMI output of the transmitter.
The displayed signal of the output port is equal to the extended video signal.
LAN
Optionally connect Ethernet devices (e.g. switch, laptop, computer etc.) to the available
Neutrik etherCON connector(s) of the extender(s). All connected devices will work as if they
are connected to the same network. Ethernet connectors are not Power over Ethernet (PoE)
compatible.
USB
Optionally connect a USB mini-B type cable between the transmitter unit and the computer in
order to control the device (in this case only the transmitter).
RS-232
Optionally for RS-232 extension: connect a controller unit (e.g. button panel) to the RS-232 port
of the transmitter with a null modem serial cable.
Power
Connect the power cord to the AC power socket to the transmitter unit. It is recommended to
power on the devices as the nal step.
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
OPT
Video processor
Media server Confidence monitor
4K projector
LCD screen
Power LW or third-party
fiber device Laptop Ethernet switch Button panel Lightware or third-party
fiber device
HDMI HDMI HDMI
Power OPT USB LAN RS-232
LAN
HDMI HDMI
OPTPower
Power
LAN
HDMI RS-232
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
OPT
Connect a multimode (MM) ber cable to the channel B of the receiver.
OPT
Optionally connect a compatible Lightware device or a third-party device to the break-out LC
connector. It is internally linked to the channel A of Neutrik connector.
HDMI
Connect an HDMI sink (e.g. 4K projector) to the HDMI 1A and the 1B output ports and the other
sink (e.g. LCD screen) to the HDMI 2 output port.
LAN
In order to control, optionally connect Ethernet devices (e.g. 4K LCD screen) to the available
Neutrik etherCON connector of the extender.
RS-232
Optionally for RS-232 extension: connect a controlled device (e.g. projector) to RS-232 port of
the receiver with a serial cable.
Power
Connect the power cord to AC power socket to the receiver unit. It is recommended to power
on the devices as the nal step.
ATTENTION! Connecting the transmitter and receiver to the same LAN beside they are connected to each
other via ber is not recommended. In case of Ethernet loop, the extenders are not available via LAN.
ATTENTION! Always use high-quality HDMI cable for connecting the sources with the transmitters, and
sinks with the receivers.

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 12
3
Product Overview
The following sections are about the physical structure of the device, input/
output ports, and connectors:
3.1. Front View
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
1Status LEDs The LEDs give feedback about the state, connections and certain settings of the
unit. For details, see Status LEDs - Transmitter Status LEDs - Receiver and section.
2Select button Transmitter: Select button toggles between the Input 1 and Input 2.
6Function button Receiver: Function button sets the output conversion mode. See the details in
Output Conversion Modes section.
3USB Port USB mini-B port for local controlling the unit by Lightware Device Controller
software.
4LCD display Transmitter: Display of the front panel menu.
5Jog dial knob Transmitter: Browse the menu by turning the knob, click on the desired item to
check or change it.
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
13 4 5
2
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
361
Ý Front View
Ý Rear View
Ý Electrical Connections
Ý Multimode Single Fiber Extender Concept
Ý Optical Interface
Ý Video and Audio Interface
Ý Control Features
3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 13
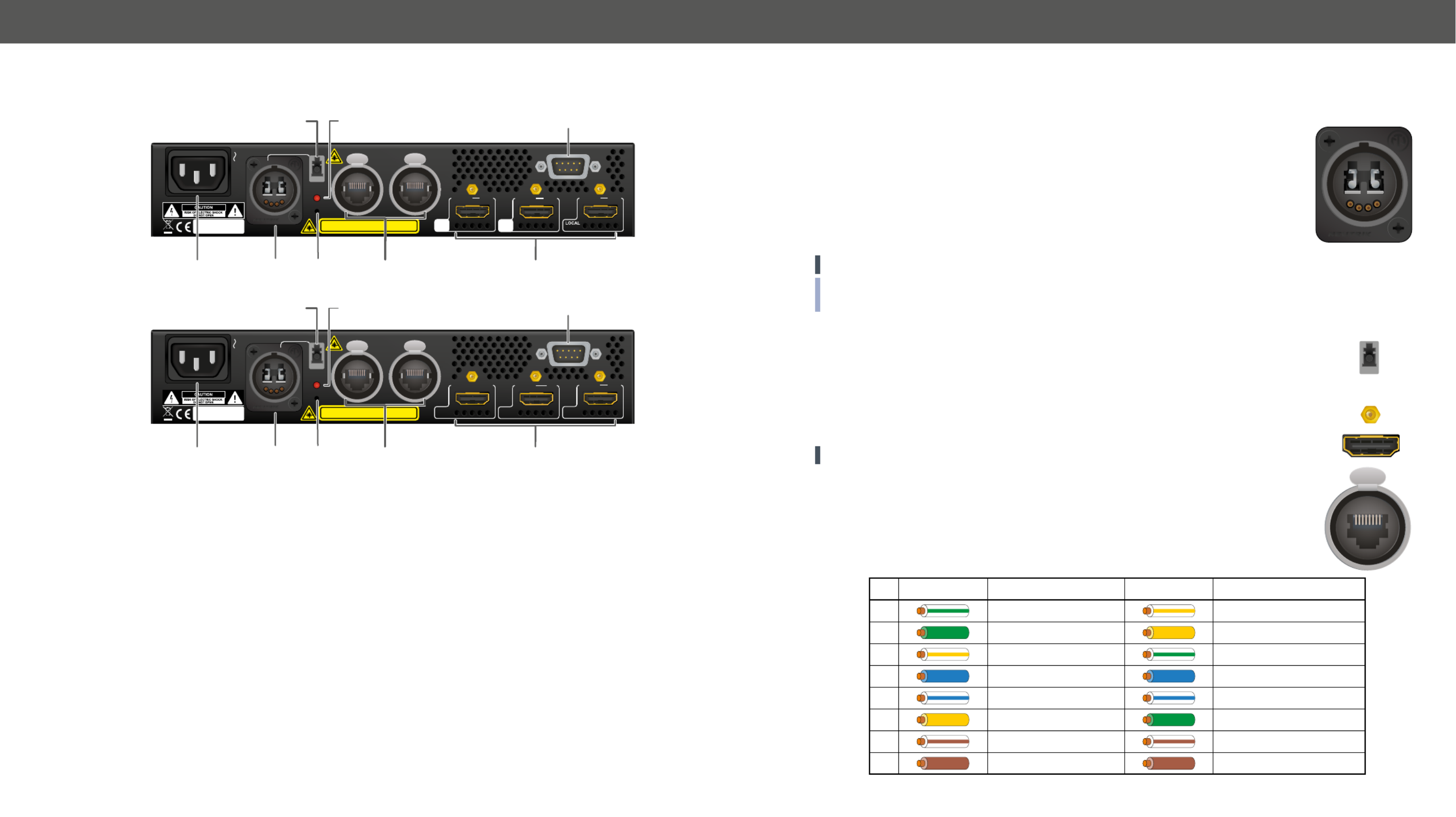
3.3. Electrical Connections
Fiber Connector
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro and HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro transmit the video, embedded
audio, Ethernet, and serial signal using multimode 50/125 ber optical cable. Neutrik
opticalCON connector (NO2-4FDW type LC duplex) and LC ODVA connector have two
ber channels, channel A and channel B. Only one channel is used (from channel A on
the transmitter to channel B on the receiver). The copper pins of the Neutrik connector
are not in use. Neutrik opticalCON DUO is compatible with 2x LC connector.
WARNING! Avoid eye exposure to beam! Direct intrabeam viewing normally hazardous.
INFO: Fiber optic cables can be easily damaged if they are improperly handled or installed. Handle the
optical cables with care to avoid damage.
LC Connector
One channel of the Neutrik connector is not used by the extenders for signal transmission
and it is internally connected to the LC break-out connector. For more information about
break-out connector see Application Example with Break-out Connector section.
HDMI Input and Output Ports
The extender provides standard 19-pole HDMI connector with screw lock.
ATTENTION! Always use high-quality HDMI cable for connecting sources and displays.
Ethernet (LAN) Port
HDMI20-OPTC series extenders are supplied Neutrik etherCON connector for Ethernet/
LAN connection. The Ethernet port can be connected to a LAN hub, switch or router by a
CATx cable. However, both cable types (straight or cross) are supported and handled by
the device, below pin assignment is recommended.
Pin TIA/EIA T568 A Color and name Color and nameTIA/EIA T568 B
1white/green stripe white/orange stripe
2green solid orange solid
3white/orange stripe white/green stripe
4blue solid blue solid
5white/blue stripe white/blue stripe
6orange solid green solid
7white/brown stripe white/brown stripe
8brown solid brown solid
3.2. Rear View
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 1 GIGABIT
ETHERNET 2
RS-232
HDMI 2.0
2
( )
18G
INPUT
HDMI 2.0
1
( )18G
INPUT
BOOT
A: FIBER OUTPUT B
LASER
ACTIVE
CAUTION - CLASS 3R INVISIBLE RADIATION
WHEN OPEN AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
0.3-0.1A
100-240 V
Sn: Made in EU, Hungary
HDMI 2.0 ( )18G
50/60 Hz AC
OUTPUT
8
4 5
1236 7
1AC connector Standard IEC connector accepting 100-240 V, 50 or 60 Hz.
2Fiber
connector
Neutrik opticalCON DUO LC connector for optical data transmission. The channel A
carries the signal from the transmitter to in the receiver.channel B
3Boot button Hidden button for special bootload function.
4Break-out
connector
The break-out LC connector is internally connected to the of Neutrik channel B
connector in the transmitter and the in the receiver. It is to carry any optical channel A
signal from the break-out LC connector.
5Laser LED It gives feedback about the operation of the optical module. When the laser is active
(Laser LED is ON), it radiates invisible waves from the optical connector. Avoid eye
exposure to beam!
6LAN Two Neutrik etherCON connectors for Gigabit Ethernet (to control the unit or for pass-
through). Both are in the same local network. Remote powering (PoE) is not possible.
7HDMI
connector
Transmitter: Two HDMI 2.0 input ports and one HDMI 2.0 output port for local display.
Receiver: Three HDMI video output ports.
8Serial port D-SUB connector for bidirectional RS-232 communication (control/command
injection/pass-through mode).
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 1 GIGABIT
ETHERNET 2
RS-232
HDMI 2.0
1B
(9G)
OUTPUT
HDMI 2.0
1A
(9G/18G)
OUTPUT
BOOT
B: FIBER OUTPUT A
LASER
ACTIVE
CAUTION - CLASS 3R INVISIBLE RADIATION
WHEN OPEN AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
0.3-0.1A
100-240 V
Sn: Made in EU, Hungary
HDMI 2.0
2
( )
18G
OUTPUT
50/60 Hz AC
8
4 5
1 2 3 6 7

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 14
USB Connector
HDMI20-OPTC series have standard USB mini-B receptacle.
RS-232 Port
The extenders have RS-232 pass-through function or can be remote controlled
through industry standard 9-pole D-SUB male connector.
D-sub connector pin assignment for standard RS-232
Pin nr. Pinout
1 NC - non-connected
2RX data receive (input)
3TX data transmit (output)
4 DTR (Internally connected to Pin 6)
5 GND signal ground (shield)
6 DSR (Internally connected to Pin 4)
7 RTS (Internally connected to Pin 8)
8 CTS (Internally connected to Pin 7)
9 NC - non-connected
INFO: HDMI20-OPTC-TX/RX220-Pro is DTE unit according to its pin-out. For more information see Serial
Management section.
INFO: Factory default settings are the same in the transmitter and receiver: 57600 Baud, 8 bit, 1stop bit, no
parity.
3.4. Multimode Single Fiber Extender Concept
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro and HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro are a HDMI 2.0 compatible single ber extender
pair. They are able to transmit digital video, embedded audio, RS-232 and Gigabit Ethernet signals via
multimode optical cable up to 700m. They are designed for rental purposes, supporting uncompressed
4K UHD resolution at 60Hz at 4:4:4 colorspace.
The extenders use only one channel of Neutrik optiCON duo cable, and the other channel is internally
connected to break-out connector. See details about in Application Example with Break-out Connector
section.
3.4.1. Summary of Interfaces - Transmitter
3.4.2. Summary of Interfaces - Receiver
Inputs: Outputs:
HDMI
Ethernet 2x
RS-232
OPTC (break-out)
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
OPTC
HDMI
+ Control Interfaces:
Inputs: Outputs:
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
+ Control interfaces:
OPTC

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 15
Application Example with Break-out Connector
Using this feature, it is possible to transmit two different A/V signal from one transmitter pair to another
receiver pair with only one Neutrik opticalCON DUO cable. See the application example below.
Transmitter Unit (HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro)
The transmitter’s laser driver sends the signal through
Channel A. Channel B is directly connected to the
break-out connector with a ber optical cable inside the
unit. Any optical signal can be transferred through this
channel in any direction.
Receiver Unit (HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro)
The receiver’s laser sensor gets the signal through
Channel B. Channel A is directly connected to the break-
out connector with a ber optical cable inside the unit.
Any optical signal can be transferred through this
channel in any direction.
B
B A
B
B A
A
B A
A
B A
LC-LC fiber
optical cable LC-LC fiber
optical cable
Neutrik opticalCON up to 700m
Source 1. Sink 1.
Sink 2.
Source 2.
A/V Video Signal 1.
A/V Video Signal 2.
HDMI HDMI
HDMI
HDMI
Transmitter side Receiver side
B A
A
BA
B A B A
A
B
B
LC-LC fiber
optical cable
LC-LC fiber
optical cable
Neutrik opticalCON up to 700m
Transmitter side Receiver side
3.5. Optical Interface
HDMI20-OPTC extenders support multimode ber optical interface to transmit or receive digital video,
embedded audio, RS-232 and Ethernet signals. For more details about the supported cable extension
distances see section.Maximum Extension Distances
Port Diagram of Optical Interface
The Neutrik opticalCON DUO cable has two ber channels, named channel A and channel B. Since Lightware
ber extenders use only one ber for signal transmission, the other ber can be used by other optical devices.
The unused ber channel is accessible by the break-out connector.
INFO: Red line shows the main direction of the video signal. The blue line represents the optical signal via
break-out connector, which direction is not specied.
B
A
HDMI
Out
B
A
A
B
Break-out
connector
Break-out
connector
Neutrik
connector
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-ProHDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
Other ber device
Neutrik
connector
HDMI
splitter
HDMI
Input 1.
HDMI
Input 2.
HDMI
splitter
HDMI
Output
2.
Video
converer
HDMI
Output
1A.
HDMI
Output
1B.
Other ber device

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 16
3.6. Video and Audio Interface
The HDMI20-OPTC series transmitter can receive signal from two types of sources:
▪ DVI-D
▪HDMI (with embedded audio)
The HDMI20-OPTC series receiver can output HDMI video signal (with embedded audio).
Port Diagram of Video and Audio Interface
Transmitter Side
The video signal is received at the Input 1 or the Input 2. The HDMI splitter duplicates the signal and sends
the same HDMI stream to the local HDMI output and the ber output.
Receiver Side
The video and the embedded audio signal arrives via optical cable into the HDMI splitter. It duplicates HDMI
stream and transmits the signal without modifying it to the HDMI Out 2 port. The HDMI splitter transmits the
same signal into the video converter where three output conversion modes can be set.
3.6.1. Output Conversion Modes
Conversion modes refer to the receiver side and this property can be set in the front panel menu of the
transmitter (see Conversion Submenu), available in the Lightware Device Controller Sofware (see HDMI
Output Port - Receiver) and also in the LW3 tree, both the transmitter and the receiver.
In Transparent mode (no conversion mode), the video signal is transmitted to the HDMI Output 1A and the
HDMI Output 1B without any changing.
INFO: Maximal data transmission capacity of Output 1B is 9 Gbps, if the video signal is above this
bandwidth, there will be no picture on the display.
Split mode means splitting of the original video signal into left and right halves and sending the split signal to
the HDMI Output 1A and the HDMI Output 1B.
In Downsample convert mode (convert to YCbCr 4:2:0) the video converter subsamples the 4:4:4 signal to 4:2:0
on the 1A and 1B Output port.
INFO: Split and downsample convert modes are available at maximum 8-bit color depth.
INPUT 1
INPUT 2 HDMI Splitter
OUTPUT 2.
Fiber OUT OUTPUT 2
OUTPUT 1A
Fiber IN
HDMI Splitter
OUTPUT 1B
Transparent
Split
Downsample
Video converter
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
3.6.2. Autoselect Feature
Besides manual crosspoint selection you can
choose the Autoselect option on the video
ports. There are three types of Autoselect as
follows:
▪ First detect mode: selected input port is
kept connected to the output while it
has an active signal
▪ Priority detect mode: always the highest
priority active input is selected to
transmit.
▪ Last detect mode: always the last attached
input is selected to transmit.
Video Interface - Example
The Concept
The HDMI signal with embedded audio comes from the Event master to Input 1. The other source is a PC,
which sends DVI-D signal to Input 2. Both of them are connected to the transmitter, where the autoselect
mode is enabled with priority 0 on the Input 1, so the Input 1 is selected.
INFO: Only one input can be selected at the same time.
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
PC
DVI-D IN
Projector
HDMI OUT
Event master
HDMI IN
OPTC INOPTC OUT
New event?
First detect Last detect
No Audio/Video
transmission
Remains
selected
Last connected
input is selected
Y
N
Current
Autoselect mode
Port with
priority 0 has a
valid signal?
Selected
port still has a
valid signal?
Priority detect
Port with
priority 1 has a
valid signal?
N
N
N
Y
YPort with priority
0 is selected
Port with priority
1 is selected
Y

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 17
3.7. Control Features
The devices can be controlled over Ethernet, USB, and RS-232 ports as well. The following sections are
about to describe the available features and settings by these interfaces.
3.7.1. USB Control Interface
The device can be controlled over front panel USB port (mini B-type connector). This interface supports LW3
protocol. The interface can be used to establish a connection to Lightware Device Controller software.
INFO: USB control operates locally, USB data is not transmitted via optical cable between the transmitter
and the receiver.
3.7.2. Ethernet Interface
The device can be controlled via Ethernet port (Neutrik etherCON connector). This interface supports any
third-party system controller with LW3 command protocol. The interface can be used to congure the device
with Lightware Device Controller and establish the connection to Lightware Device Updater software and
perform rmware upgrade.
Two Neutrik etherCON connectors provide a wide range of application possibilities:
▪ Control the device
▪ Firmware upgrade
▪ Create a local network
▪ Daisy chain connection
Port Diagram of Ethernet Interface
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 1
Fiber OUT Fiber IN
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 2
Gigabit
Ethernet
Switch
CPU
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 1
GIGABIT
ETHERNET 2
Gigabit
Ethernet
Switch
CPU
LINK
Ethernet Interface - Example
Transmitters receivers transmitters are connected to each other via LAN, the connected to the via optical ber
and all the connected to the via LAN.projectors receivers
This way the can control the system with Ethernet commands:Laptop
▪ HDMI20-OPTC.TX220-Pro (1-3.).
▪ HDMI20-OPTC.RX220-Pro (1-3.).
▪ Projector (1-6.).
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro 1. HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro 1.
Laptop
Projector 1.
Projector 2.
Projector 3.
Projector 4.
Projector 5.
Projector 6.
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro 2.
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro 3.
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro 2.
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro 3.
LAN
Optical fiber

3. Product Overview HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 18
3.7.3. Serial Interface
INFO: HDMI20-OPTC-TX/RX220-Pro are DTE unit according to their pin-out. For more details about pin
assignment see section.RS-232 Port
Serial data communication can be established via local RS-232 port (D-SUB male connector). Three different
RS-232 modes can be set for the serial port: pass-through mode, control mode, command injection mode,
see the gure below.
Port Diagram of Serial Interface
The following operation modes are dened:
▪ PASS: Pass-through modeThe local serial port is in .
▪ CONTROL: Control modeThe local serial port is in .
▪ CI: Command Injection mode The local serial port is in .
Pass-through Mode
In pass-through mode, the given device forwards the data that is coming from one of its ports to another
same type of port. The command is not processed by the CPU. Incoming serial data is forwarded from one
port to another port.
ATTENTION! Both the transmitter and the extender have to be set , in case of sending Pass-through mode
RS-232 commands from the TX side to the third party device on the RX side.
Control Mode
The incoming data from the given local port is processed and interpreted by the CPU. The mode allows to
control the extender directly. LW3 protocol commands are accepted.
Operation
mode
Fiber
Ethernet
RS-232
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
LINK
RS-232 /
OPTC converter
CPU
Device control
(local serial)
Ethernet
Switch
RS-232 /
TCP converter
Device control
(IP)
PASS
CONTROL
CI
Fiber
RS-232 /
OPTC converter
CPU
Device control
(local serial)
Ethernet
Switch
RS-232 /
TCP converter
Device control
(IP)
Operation
mode
Ethernet
RS-232
PASS
CONTROL
CI
Command Injection Mode
In this mode, the extender works as a TCP/IP <-> RS-232 bidirectional converter. The TCP/IP data signal
is converted to RS-232 data and vice versa. TCP/IP port numbers are dened for the serial ports for this
purpose. E.g. the default Command Injection port number of the local RS-232 port is 8001.
INFO: The commands in this mode not transmitted via ber, they operates between the local ports.
RS-232 Signal Transmission - Example 1
The Concept
You can control the over the extenders with the . The controller is connected to Projector System controller
the local RS-232 port of the which transmits the signal toward the Transmitter Receiver over the ber optical
line. The Projector is connected to the local RS-232 port of the . The serial connection is bidirectional Receiver
which means the controller gets back the responses of the projector.
In this case the RS-232 port of the transmitter and receiver has to be set to .Pass-through mode
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTRO L
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> Sys tem Se ttings
Ports
E DID
H ealth
Re mote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTRO L
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
4. Operation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 19
4
Operation
This chapter is about the powering and operating of the device describing the
functions which are available by the front/rear controls:
Ý
Ý
Ý
4.1. Powering on
Connect the power cord to the AC input connector; the extender is
loaded automatically.
4.2. Front Panel Operations
ATTENTION!
though the device is fully functional.
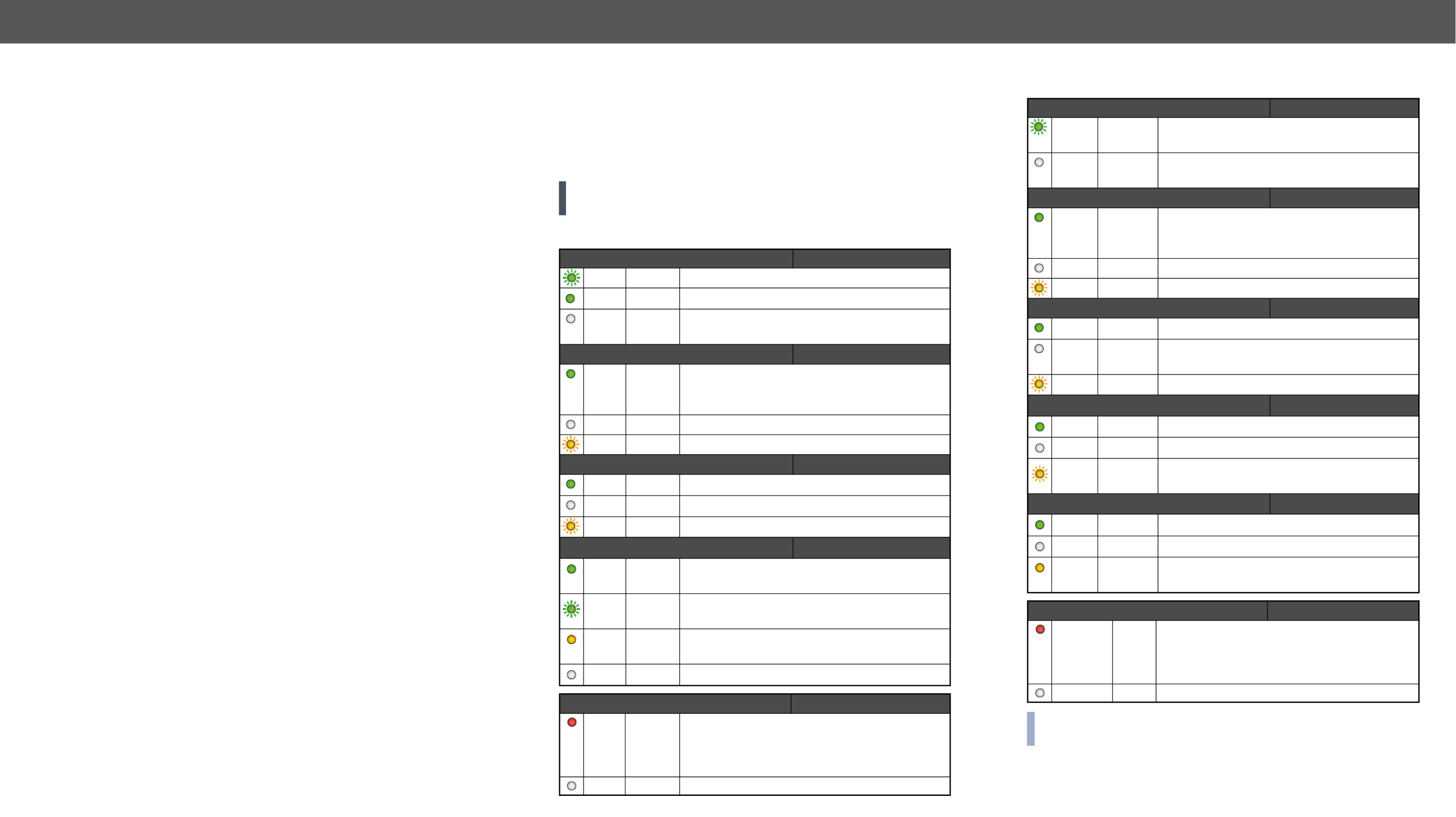
Status LEDs - Transmitter
POWER/LIVE FRONT
green blinking The transmitter unit is powered and ready to use.
green on The transmitter unit is out of operation.
off The transmitter unit is NOT powered or out of
operation.
FIBER LINK FRONT
green on The connection is established between the
transmitter and the receiver and they can
communicate to each other.
off
yellow blinking
HDCP FRONT
green on
off There is no HDCP encryption in the video signal.
yellow blinking It shows HDCP error.
INPUT1, INPUT2 FRONT
green on This port is selected and there is a valid video
signal on it.
green blinking
video signal on it.
yellow on
valid video signal on it.
off This port is not selected and there is no signal on it.
LASER ACTIVE REAR
red on It gives feedback about the operation of the
optical module, that means the laser radiates
invisible waves. Avoid direct eye contact with
the optical connectors!
off Laser module is not active.
Status LEDs - Receiver
POWER/LIVE FRONT
green blinking The receier unit is powered and ready to
use.
off The receier unit is NOT powered or out of
operation.
FIBER LINK FRONT
green on The connection is established between the
transmitter and the receiver and they can
communicate to each other.
off
yellow blinking
HDCP FRONT
green on
off There is no HDCP encryption in the video
signal.
yellow blinking It shows HDCP error.
SIGNAL PRESENT FRONT
green on
off No video signal is present.
yellow blinking It shows error in the video signal
transmission.
OUTPUT CONVERSION FRONT
green on Split mode is active.
off Transparent mode (no conversion) is active.
yellow on Downsample convert (convert to YCbCr
4:2:0) mode is active.
LASER ACTIVE REAR
red on It gives feedback about the operation of the
optical module, that means the laser radiates
invisible waves. Avoid direct eye contact with
the optical connectors!
off Laser modul is not active.
Function button, they show that the front panel lock is enabled.

4. Operation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 20
4.2.1. Function Button - HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
Select button is for switching between the Input 1 and the Input 2.
Autoselect mode can not be activated by pushing the Select button, but
this function can be disabled by choosing Input 1 or Input 2 with the
Select button.
INFO: Autoselect mode can be set with Lightware Device Controller
software (see HDMI Output Port - Transmitter Optical Output and
Port - Transmitter section) or with protocol commands (see
Changing the Autoselect Mode section).
Enable Dynamic (DHCP) IP Address
The device gets a static IP address as a factory default setting. If
this setting does not t to the circumstances during install or usage,
DHCP* can be enabled from the front panel:
Step 1. Make sure the device is powered on and operational.
Step 2. Press and keep pressed the button for 5 seconds.Select
Step 3. After 5 seconds front panel LEDs start blinking; release the
button and press it 3 times again quickly (within 1,5 seconds).
Step 4. The LEDs get dark, DHCP gets enabled.
Step 5. As a nal step, device restarts and is available with the new IP
address.
* Static IP address also can be modied. This setting is available on
the front panel menu or in Lightware Device Controller software.
Restore Factory Default Settings
To restore factory default values, do the following steps:
Step 1. Make sure the device is powered on and operational.
Step 2. Press and keep pressed the button for 10 seconds. After Select
5 seconds front panel LEDs start blinking but keep on pressing
the button.
Step 3. After 5 seconds the blinking gets faster; release the button and
press it 3 times again quickly (within 1,5 seconds).
Step 4. The LEDs get dark, the device restores the factory default
settings and reboots.
Factory default settings are listed in the Factory Default Settings
section.
4.2.2. Boot Button
Hidden button for special bootload function. Use only for the particular
request of the Lightware Support Team.
4.2.3. Function Button - HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
Function button sets the output conversion mode. See details
about these modes in section.Output Conversion Modes
Enable Dynamic (DHCP) IP Address
The device gets a static IP address as a factory default setting. If this
setting does not t to the circumstances during install or usage, DHCP
can be enabled from the front panel:
Step 1. Make sure the device is powered on and operational.
Step 2. Press and keep pressed the button for 5 seconds.Function
Step 3. After 5 seconds front panel LEDs start blinking; release the
button and press it 3 times again quickly (within 1,5 seconds).
Step 4. The LEDs get dark, DHCP gets enabled.
Step 5. As a nal step, device restarts and is available with the new IP
address.
* Static IP address also can be modied. This setting is available on
the front panel menu or in Lightware Device Controller software.
Restore Factory Default Settings
To restore factory default values, do the following steps:
Step 1. Make sure the device is powered on and operational.
Step 2. Press and keep pressed the button for 10 seconds. Function
After 5 seconds front panel LEDs start blinking but keep on
pressing the button.
Step 3. After 5 seconds the blinking gets faster; release the button and
press it 3 times again quickly (within 1,5 seconds).
Step 4. The LEDs get dark, the device restores the factory default
settings and reboots.
Factory default settings are listed in the Factory Default Settings
section.
4.2.4. Boot Button
Hidden button for special bootload function. Use only for the particular
request of the Lightware Support Team.

4. Operation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 21
4.3. Front Panel LCD Menu Operations
The front panel has a color LCD that shows the most important
settings and parameters structured in a menu. The jog dial control
knob can be used to navigate between the menu items or change the
value of a parameter. The knob can be pressed to enter a menu or
edit/set a parameter.
Parameter Selection
The blue colored line means the selected
menu/parameter, the green one means the
current setting.
TIPS AND TRICKS: The faster you rotate
the jog dial, the faster the parameter list is
scrolled.
System Settings
Network
RS-232
Front panel
Device Info
Factory Defaults
Reset Device
Bootload Mode
Ports
I1,12,O1,O2
Video Status
Video Settings
EDID
View
Switch
Save
Health
Operation
Temperatures
Voltages
Remote
Conversion
Output 1/A +5V
Output 1/B +5V
Output B +5V
Dark Mode
Network
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
DARK MODE
> Enabled
Disabled
« Back
4.3.1. System Settings Menu
Network Submenu
The parameters of the network connection
can be set in this submenu. IP, Subnet,
Gateway and MAC parameters show the
current settings. If the DHCP option is
disabled, three more parameters are listed
which can be set for a static IP address:
▪Static IP,
▪Static Subnet,
▪Static Gateway.
ATTENTION! If you change the network settings, always press the
Save option under Network menu (not only in the submenu of the
parameter) to apply the new settings.
RS-232 Submenu
Adjustable parameters of the local RS-232
port:
▪Mode (Pass-through/ Control/
Command injection),
▪Baud Rate (4800/ 7200/ 9600/ 14400/
19200/ 38400/ 57600/ 115200)
▪Protocol (LW2/ LW3).
Front Panel Submenu
The following front panel-related parameters
can be set in this submenu:
▪Display Backlight (1-10)
The brightness of the LCD can be set from 1
to 10 on a scale.
▪Dark Mode (Enabled/ Disabled)
All the LEDs and the background light of the LCD on the transmitter
unit are turned off 60 s after enabling the dark mode.
TIPS AND TRICKS: Press any buttons or turn the jog dial knob to
"wake up" the device. The rst contact activates the LEDs and LCD
and does not execute the original function.
INFO: The setting of the dark mode in the receiver is available in the
Remote Menu.
▪Rotary Direction (CW Down/ CCW Down)
NETWORK
> IP
192.168.0.101
Subnet
255.255.255.0
« Back Save
RS-232
> Mode
Passthrough
Baud rate
57600
« Back Save
DISPLAY BACKLIGHT
9
0 2 4 6 8 10
☼
☼
Device Info Submenu
In this submenu you can check basic
information about the transmitter unit:
▪Serial number
▪Hardware Version
▪Firmware Version
▪Video MCU #1
▪Video MCU #2
Factory Defaults Submenu
Factory default settings will be restored by
choosing .Yes
Reset Device Submenu
There is a possibility to reset the device.
Bootload Mode Submenu
Special function for entering the bootload
mode.
DEVICE INFO
> Serial Number
00005001
Hardware Version
V11_AAA0
« Back
FACTORY DEFAULTS
Are you sure you
want to proceed?
« No Yes
RESET DEVICE
Are you sure you
want to reboot
the device?
« No Yes
BOOTLOAD MODE
Are you sure you
want to enter
bootload mode?
« No Yes

4. Operation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 22
Video Settings Submenu for Input Ports
▪I1: HDCP Enable (Disabled / HDCP 1.4
only / HDCP 2.2 or 1.4 )
▪I2: HDCP Enable (Disabled / HDCP 1.4
only )
Video Status Submenu for Output Ports
The most important status information can
be seen of the chosen output port.
The table below relates to the output ports
of both the transmitter and receiver.
Parameter O1 (OPTOUT ) O2 (HDMIOUT)
Hotplug detect Present/ Not present Present/ Not present
Signal Present Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Present/ Not present/
Unknown
HDCP Status none/ HDCP 1.4/HDCP 2.2 none/ HDCP 1.4/ HDCP 2.2
HDCP
capability -none/ HDCP 1.4/ HDCP 2.2
Embedded
Audio
Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Pixel Clock
(MHz) No signal [x] MHz No signal [x] MHz
Active
Resolution
Unknown/ No signal
[x] [y][i\|p][f]x
Unknown/ No signal
[x] [y][i\|p][f]x
Total
Resolution
Unknown/ No signal/
[x] [y]x
Unknown/ No signal/
[x] [y]x
Video Settings Submenu for Output Ports
▪Signal Type (Auto / DVI)
▪+5V Enable (Always on / Always off
/ Auto)
▪HDCP Mode (Auto / Always on)
HDCP ENABLE
> Disabled
HDCP 1.4 only
HDCP 2.2 or 1.4
« Back
VIDEO STATUS
> Hotplug detect
Present
Signal Present
Present
« Back
VIDEO SETTINGS
> Signal Type
Auto
+5V Enable
Always on
« Back
4.3.3. EDID Menu
Advanced EDID Management is available in the front panel LCD
menu which allows to view an EDID, switch, or save it to the User
EDID memory. See more information about EDID technology in EDID
Management. The EDID memory structure of the device can be found
in chapter.Sources and Destinations
View Submenu
Select the desired EDID memory block:
Factory EDIDs, Last Attached EDIDs, User EDIDs,
or Emulated EDIDs. Select the Name item and
press the knob. Use the jog dial to step
between the EDIDs. The following information
can be checked:
▪Preferred Resolution
▪Monitor Name
▪Audio Info
Switch Submenu
The submenu looks similar to the View
submenu but in this case, the Destination
is also listed. To change an EDID do the
followings:
Step 1. EDID/SwitchNavigate to the submenu.
Step 2. NameSelect the item and press the
knob. Use the jog dial to select the
desired (F1-F146, U1-U14, or D1-D2) and press the knob.EDID
Step 3. DestinationSelect the item and press the knob. Use the jog dial
to select the desired (E1, E2, All) and press the EDID memory
knob.
Step 4. SwitchNavigate to the option and press the knob.
Save Submenu
The EDID of a connected sink can be saved to
the User EDID memory as follows:
Step 1. Navigate to the EDID/Save submenu.
Step 2. Select the Name item and press the knob.
Use the jog dial to select the desired
EDID (D1-D2*) and press the knob.
Step 3. DestinationSelect the item and press the knob. Use the jog dial
to select the desired (U1-U14) and press the knob.EDID memory
Step 4. SaveNavigate to the option and press the knob.
* D1 is for Optical output and D2 is for local HDMI output.
FACTORY EDIDS
F133
4096X2160P60.00Hz
4Kp_60_420
2chLPCM
« Back
SWICH
F133 E1
4096X2160P60.00Hz
4Kp_60_420
2chLPCM
« Back Switch
SAVE
D1 U14
1920x1080p60.00Hz
Univ_HDMI_PCM
2chLPCM
« Back Save
4.3.2. Ports Menu
When entering the menu the available video
input and output ports are listed. The icons
display information about the port and the
video signal (see below table). Select the
desired port and enter to see the submenu.
Grey
icon Description White
icon Description
Source/sink is not
connected Source/sink is
connected
No audio signal in the
video stream Audio is embedded in
the video stream
Signal is presentnot Signal is present
Signal is encryptednot
with HDCP Signal is encrypted
with HDCP
The port is unmuted The port is muted
Video Status Submenu for Input Ports
The most important status information can
be seen of the chosen input port.
The table below relates to the input ports of
both the transmitter and receiver.
Parameter I1 I2
+5V present Present/ Not present Present/ Not present
Signal Present Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Present/ Not present/
Unknown
HDCP Status none/ HDCP 1.4/HDCP 2.2 none/ HDCP 1.4
Embedded Audio Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Present/ Not present/
Unknown
Pixel Clock (MHz) No signal/ [x] MHz No signal/ [x] MHz
Active Resolution Unknown/ No signal/
[x] [y][i\|p][f]x-
Total Resolution Unknown/ No signal/
[x] [y]x-
PORTS
> I1
I2
O1
O2
« Back
VIDEO STATUS
> +5V present
Present
Signal Present
Present
« Back

4. Operation HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 23
4.3.4. Health Menu
Operation Submenu
The following information is displayed about
the transmitter unit in this menu:
▪ Uptime: the elapsed time since the last
booting.
▪ Operation time: displays the summary
of the operation hours.
Temperatures Submenu
This submenu gives a feedback about the current temperatures of the
internal parts in the unit:
▪ CPU / System / Air intake / Video chip / Ethernet switch / Video
MCU #1 / Video MCU #2.
Voltages Submenu
The following information is displayed in Voltages Submenu:
▪ Main 5V / Main 3.3V, Video IC #11.3V V/1 / Video IC #11.3V V/2
/ Video IC #2 1.3V/1 / Video IC #2 1.3V/2
4.3.5. Remote Menu
ATTENTION! This settings related to the connected .receiver
Adjustable parameters of the receiver:
Conversion Submenu
The following conversion modes can be set in the receiver:
▪ Off
▪ YUV 4:2:0
▪ Split left/right
▪ Split right/left
See more details about this mode in Output Conversion Modes
section.
OPERATION
> Uptime
0 days 02:33:23
Operation Time
5 days 06:12:44
« Back
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
transmitter
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
receiver
Output 1/A +5V, Output 1/B +5V, Output 2 +5V Submenu
▪ Always on
▪ Always off
▪ Auto
Dark Mode (Enabled/Disabled) Submenu
All the LEDs on the receiver unit are turned off 60 seconds after
enabling the dark mode. Waking up the device is available by disabling
the dark mode.
Network Submenu
The parameters of the 's network receiver
connection can be set in this submenu.
IP, Subnet, Gateway and MAC parameters
show the current settings. If the DHCP
option is disabled, three more parameters
are listed which can be set for a static IP
address:
▪ Static IP,
▪ Static Subnet,
▪ Static Gateway.
ATTENTION! If you change the network settings, always press the
Save option under Network menu (not only in the submenu of the
parameter) to apply the new settings.
NETWORK
> IP
192.168.0.102
Subnet
255.255.255.0
« Back Save
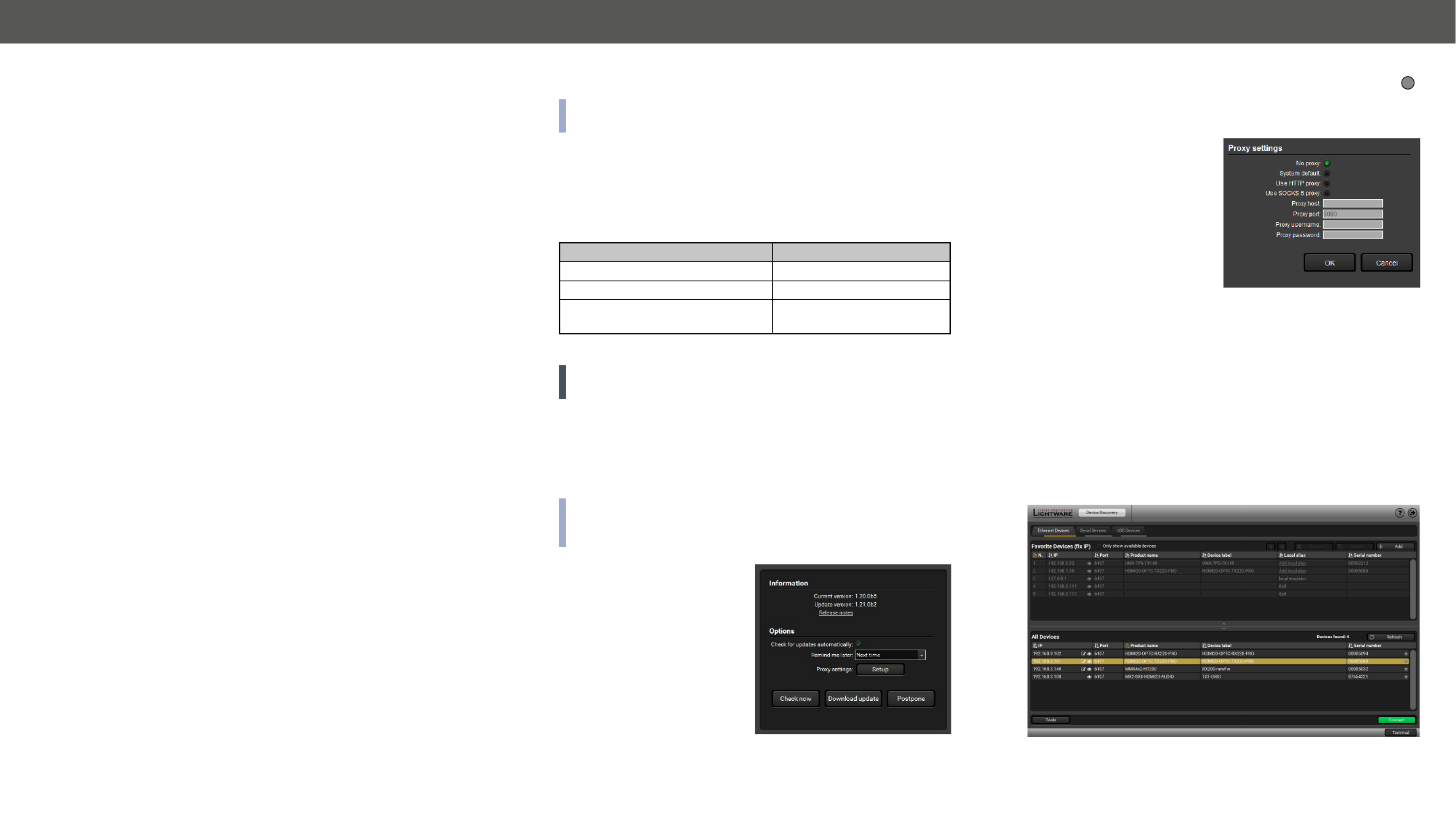
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 24
5
Software Control – Using Lightware Device
Controller
The extender can be controlled by a computer through the LAN, RS-232 and
USB ports using Lightware Device Controller (LDC). The software can be
installed on a Windows PC or Mac OS X. The application can be downloaded
from www.lightware.com. The Windows and the Mac versions have the same
look and functionality.
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
5.1. Install and Upgrade
has the same look and functionality.
Installation for Windows OS
Run the installer. If the User Account Control drops a pop-up message
click .Yes
During the installation you will be prompted to select the type of the
installation: and the install:normal snapshot
Normal install Snapshot install
The installer can update only this instance Cannot be updated
Only one updateable instance can exist
for all users
More than one different version
can be installed for all users
Comparison of installation types
ATTENTION! Using the Normal install as the default choice is highly
recommended.
Installation for Mac OS X
over the Applications icon to copy the program into the Applications
folder. If you want to copy the LDC into another location just drag the
icon over the desired folder.
INFO: The MAC installer is equal with the Normal install in case
attributes.
Upgrading of LDC
Step 1. Run the application.
The Device Discovery window
appears automatically and the
program checks the available
updates on Lightware’s website
and opens the update window if
the LDC found updates.
The current and the update
version number can be seen at
the top of the window and they
are shown in this window even with the snapshot install.
The Update window can also be opened by clicking the About icon
and the button.Update
Set the desired update setting in the section.Options
▪ If you do not want to
check for the updates
automatically, uncheck the
circle, which contains the
green tick.
▪ If you want to postpone
the update, a reminder
can be set with different
delays from the drop down
list.
▪ If the proxy settings traverse the update process, set the proper
values then click the button.OK
Step 2. Download updateClick the button to start the upgrading.
The updates can be checked manually by clicking the Check now
button.
5.2. Establishing the Connection
Step 1. Connect the device to a computer via USB, RS-232 or Ethernet.
Step 2. Run the controller software; device discovery window appears
automatically.
Device Discovery Window in LDC
?

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 25
Step 3. Select the unit from the discovered Ethernet devices or under USB devices; when the device is
connected through RS-232 click on the button next to the desired serial port to display the Query
device’s name and serial number. Double click on the receiver or select the device and click on the
Connect button.
ATTENTION! When the device is connected via the local RS-232 port, make sure that Control mode and
LW3 protocol are set on the serial port.
Change IP Address
To modify IP address settings quickly it is not necessary to enter the device's
settings/network menu, you can set them by clicking the pencil icon beside
the IP address. In this window you can see only the new settings.
Identifying the Device
Clicking on the icon results the blinking of the LDC screen for 10 seconds. The
feature helps to identify the device itself in the rack shelf.
5.3. Crosspoint Menu - HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
Video tab
Video Tab in Crosspoint Menu
1
3
5
4
2
7
8
6
1Main menu The available menu items are displayed. The active one is shown with dark grey
background color.
2Information ribbon It shows the device label which can be edited in the Settings menu - Status Tab.
A drop-down menu is displayed by clicking on this ribbon. You can turn back to the
Device Discovery Window or open the connected TX or RX in a new window (if it is in
the same LAN).
3Tab selector ribbon Submenu selection by clicking on the tab.
4Input ports Click on the port to open the Port properties window.
5Connections Light grey square means the port is available but there is no connection between the
input and the output. White square means there is a connection between the input and
the output port.
6Output ports Click on the port to open the Port properties window.
7Advanced view Click on the button to display the Advanced view page. It shows the Terminal window
and the LW3 protocol tree.
8Legend panel The applied colors of the input/ output ports are described in this panel.
Port Tiles
The colors of the port tiles and the displayed icons represent different states and information:
OPTOUT
A5
1 3
O2
4
2
State Indicators
Icon Icon is grey Icon is black
Source/sink is Source/sink is connected (+5V / Hotplug detected)not connected
Audio is embedded in the video not
stream Audio is embedded in the video stream
Port is unmuted Port is muted
HDCP encryption is enabled HDCP encryption is enablednot
Icon Icon is grey Icon is green
A
Autoselect setting is disabled Autoselect setting is enabled
1Port name
2Port icon
3Port number
4Signal present indicator
green grey: present / : not present
5State indicators
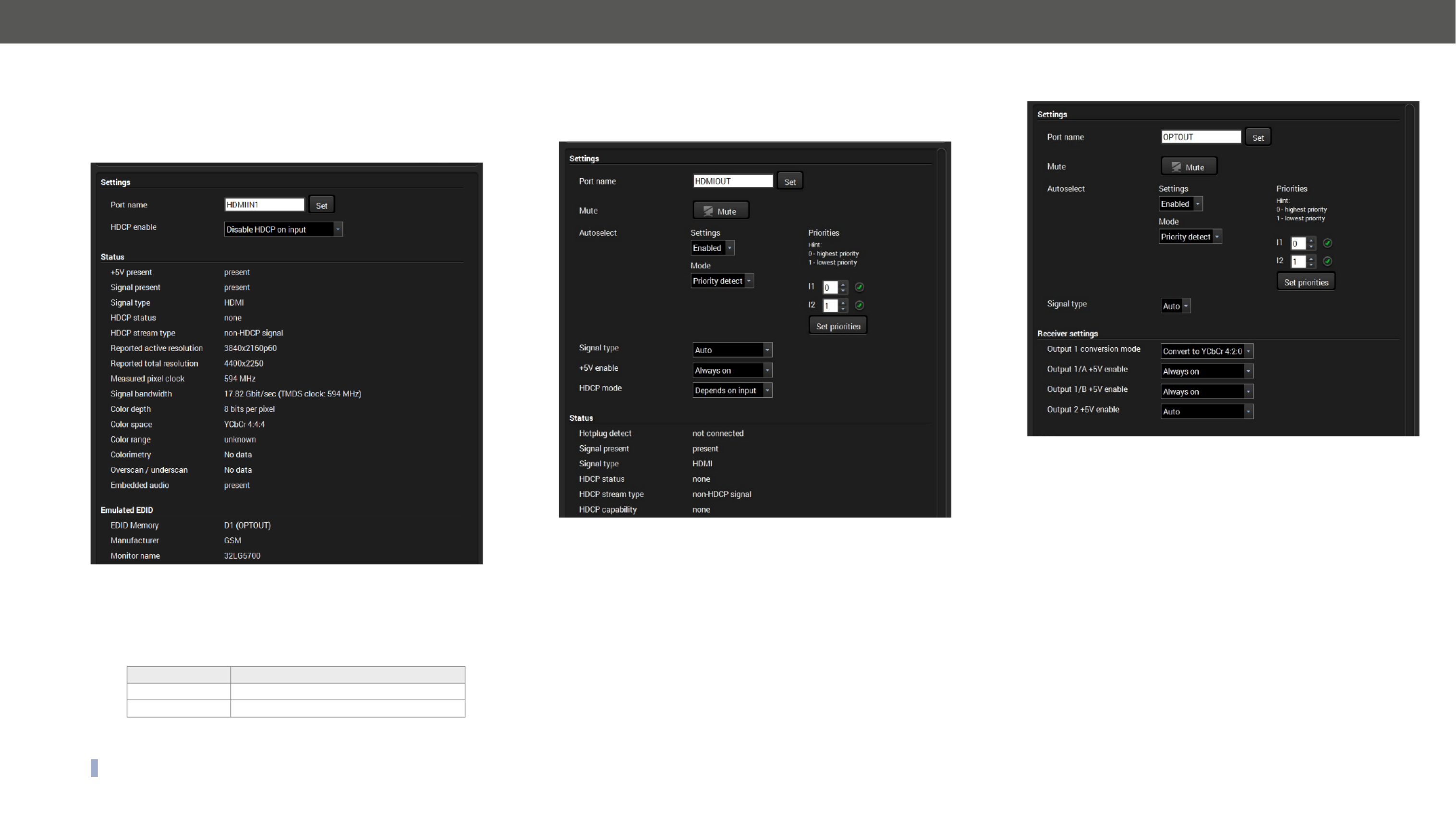
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 26
5.4. Port Properties Window
5.4.1. HDMI Input Port -Transmitter
By clicking on one of the HDMI input tile, the most important video related
information and settings are available in the port properties window.
Available Settings:
▪ Port name
▪ HDCP Enable (Disable HDCP input / Allow HDCP 1.4 only /
Allow HDCP 2.2 and HDCP 1.4).
Port number max. HDCP version
I1 HDCP 2.2
I2 HDCP 1.4
▪ Reloading factory defaults (see more details in Factory Default
Settings section).
INFO: Factory default settings have not effect on the emulated EDID.
5.4.2. HDMI Output Port - Transmitter
Click on the local HDMI output port to open the port properties window. The
most important information and settings are available from the panel.
Available settings:
▪ Change the name of the port;
▪ Mute/unmute the port;
▪ Autoselect settings: enable / disable, mode, and priorities. (See
more details in Autoselect Feature section)
▪ Auto/DVI/HDMI signal type;
▪ Enabling the +5V: Auto / Always on / Always off;
▪ HDCP mode: Depends on input / Maximum possible
Depends on input: The encryption level depends on the settings of the
input port and the source content/device. If the incoming signal is not
encrypted, then the outgoing signal will not be encrypted either.
Maximum possible: The highest supported level of encryption.
▪ Factory default settings for the selected port.
Optical Output Port - Transmitter
Available settings (related to the transmitter):
▪ Change the name of the port;
▪ Mute/unmute the port;
▪ Autoselect settings: enable / disable, mode, and priorities. This
setting is always the same on both outputs. (See more details
in Autoselect Feature section)
▪ Auto/DVI/HDMI signal type;
▪ Factory default settings for the selected port.
Available settings (related to the receiver):
▪ Output 1 conversion mode: No conversion / Convert to YCbCr
4:2:0 / Split A: left, B: right / Split A: right, B: left. For more
information see section.Output Conversion Modes
▪ Output 1/A +5V enable: Auto / Always on / Always off
▪ Output 1/B +5V enable: Auto / Always on / Always off
▪ Output 2 +5V enable: Auto / Always on / Always off

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 27
5.4.3. Optical Input Port - Receiver
Available Settings:
▪ Port name;
▪ Reloading factory defaults (see factory default settings in the
Factory Default Settings section).
INFO: Factory default settings have not effect on the emulated EDID.
5.4.4. HDMI Output Port - Receiver
Available Settings:
▪ Change the name of the port;
▪ Mute/unmute the port;
▪ Auto/DVI/HDMI signal type;
▪ Enabling the +5V: Auto / Always on / Always off
▪ HDCP mode: Depends on input / Maximum possible
Depends on input: The encryption level depends on the settings of the
input port and the source content/device. If the incoming signal is not
encrypted, then the outgoing signal will not be encrypted either.
Maximum possible: The highest supported level of encryption.
▪ Output 1 conversion mode: No conversion /
Convert to YCbCr 4:2:0 / Split A: left, B: right / Split A: right, B: left.
For more information see Output Conversion Modes section.
INFO: Conversion mode setting effects only on HDMIOUT1A (O1)
and HDMIOUT1B (O2) port, so HDMIOUT2 (O3) port does not have
not this setting.
▪ Factory default settings for the selected port.

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 28
5.5. EDID Menu
Advanced EDID Management can be accessed by selecting the EDID menu. There are two panels: left one
contains , right one contains slots where the EDIDs can be emulated or copied.Source EDIDs Destination
Control buttons
Export Exporting an EDID (save to a
le)
Executing EDID emulation or
copying (Transfer button)
Import Importing an EDID (load from a
le) Delete selected Deleting EDID (from User
memory)
Info Display EDID Summary window Select all Selecting all memory places
in the right panel
Edit Opening Advanced EDID Editor
with the selected EDID Select none
Selecting none of the
memory places in the right
panel
Create Opening Easy EDID Creator
5.5.1. Sources and Destinations
The EDID memory consists of four parts:
▪ Factory EDID list (F1-F146) the pre-programmed EDIDs, see the Factory EDID List in the Appendix section.
▪ Dynamic EDID list (D1-D2): the EDID of the last attached display device. The extender stores the last
EDID from the previously connected sink on each output port. Thus, an EDID can be shown even if
there is no device is connected to the output port at that moment.
▪ User memory locations (U1 – U14): they can be used to save custom EDIDs. Any EDID from the User/
Factory/Dynamic EDID lists can be copied to the user memory.
▪ Emulated EDID list (E1-E2): the currently emulated EDID for the input. The source column displays
the memory location that the current EDID was routed from. The source reads the EDID from the
Emulated EDID memory on the input port.
There are two types of emulation: and .static dynamic
▪ Static EDID emulation: an EDID from the Factory or User EDID list is selected. Thus, the Emulated EDID
remains the same until the user emulates another EDID.
▪ Dynamic EDID emulation: it can be enabled by selecting D1-D2 EDID memory. The attached monitor’s
EDID is copied to the input; if a new monitor is attached to the output, the emulated EDID is changed
automatically.
INFO: The default emulated EDID is D1 both the transmitter and the receiver. The EDID, which is from the
attached monitor of HDMIOUT1A (O1) port of the receiver, is copied to all the input ports.
5.5.2. EDID Operations
Changing the Emulated EDID
Step 1. Factory, Dynamic User EDIDChoose the desired tab ( , or EDID list) on the left panel and select an .
Step 2. EmulatedSelect the tab on the right panel.
Step 3. Select the target port on the right panel (one or more ports can be selected); the EDID(s) will be
highlighted with a yellow cursor.
Step 4. TransferPress the button to change the emulated EDID.
Learning an EDID
The process is the same as changing the emulated EDID; the only difference is the panel: press Destination
the User button. Thus, one or more EDIDs can be copied into the user memory either from the factory memory
or from a connected sink (Dynamic).
Exporting an EDID
Source EDID can be downloaded as a le (*.bin, *.dat or *.edid) to the computer.
Step 1. EDID left panel Select the desired from the (the line will be highlighted with yellow).
Step 2. ExportPress the button to open the dialog box and save the le to the computer.
Export
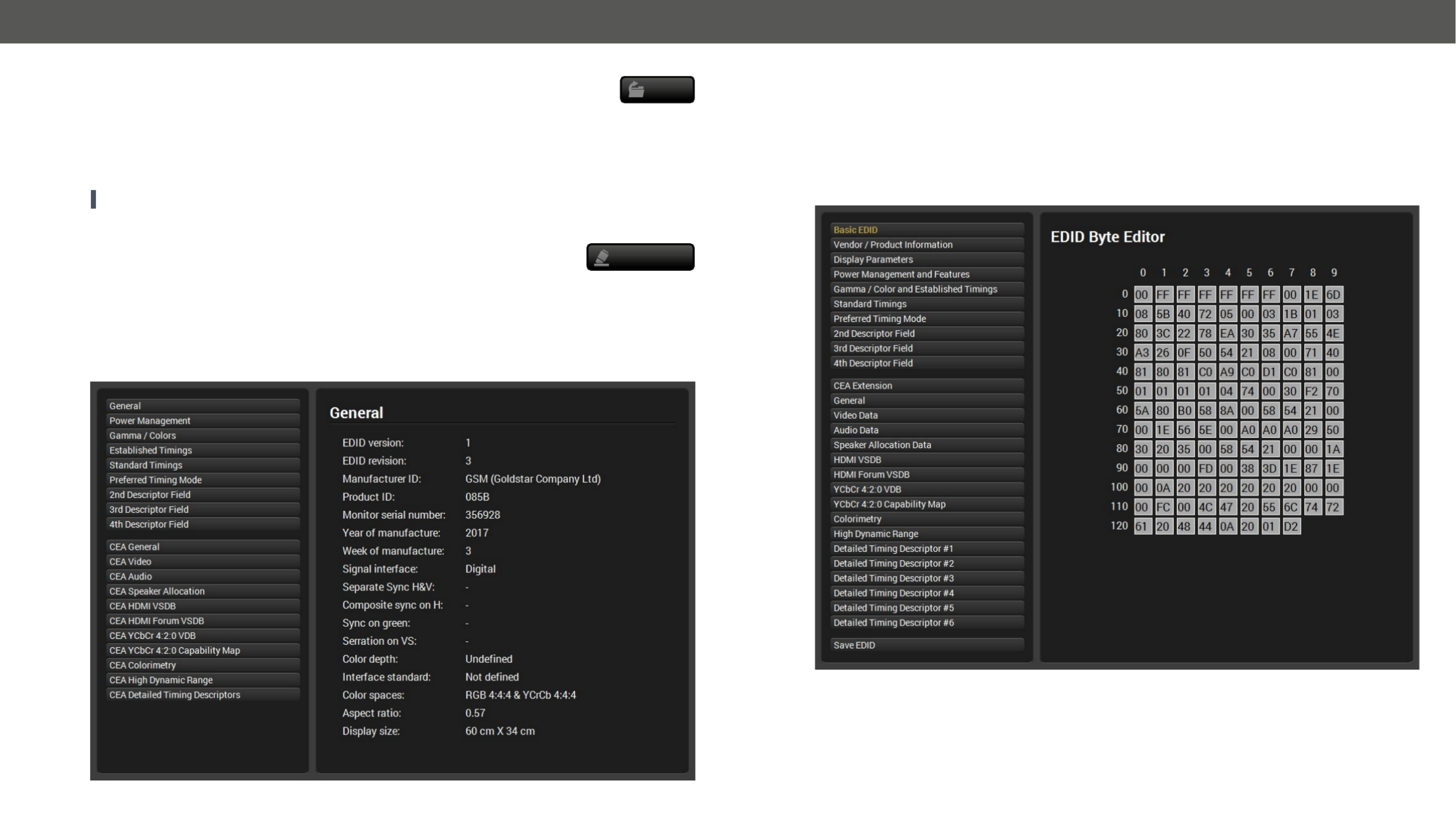
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 29
Importing an EDID
Previously saved EDID (*.bin, *.dat or *.edid le) can be uploaded to the user memory:
Step 1. UserSelect the tab in the left panel and select a memory slot.
Step 2. Import Press the button below the Source panel.
Step 3. Browse the le in the opening window then press the Open button. Browsed EDID is imported into the
selected User memory.
ATTENTION! The imported EDID overwrites the selected memory place even if it is not empty.
Deleting EDID(s)
The EDID(s) from User memory can be deleted as follows:
Step 1. UserSelect the tab in the left panel.
Step 2. Select the desired memory slot(s); one or more can be selected (Select all Select None and buttons can
be used). The EDID(s) will be highlighted with yellow.
Step 3. Deleted selectedPress the button to delete the EDID(s).
5.5.3. EDID Summary Window
Select an EDID from Source panel and press the button to display EDID summary.Info
Import
Delete selected
5.5.4. Editing an EDID
Select an EDID from the left panel and press the button to display Advanced EDID Editor window. The Edit
editor can read and write all descriptors, which are dened in the standards, including the additional CEA
extension. Any EDID from the device’s memory or a saved EDID le can be loaded into the editor. The software
resolves the raw EDID and displays it as readable information to the user. All descriptors can be edited, and
saved in an EDID le, or uploaded to the User memory. For more details about EDID Editor please visit our
website (www.lightware.com) and download the EDID Editor User's Manual.
EDID Editor Window
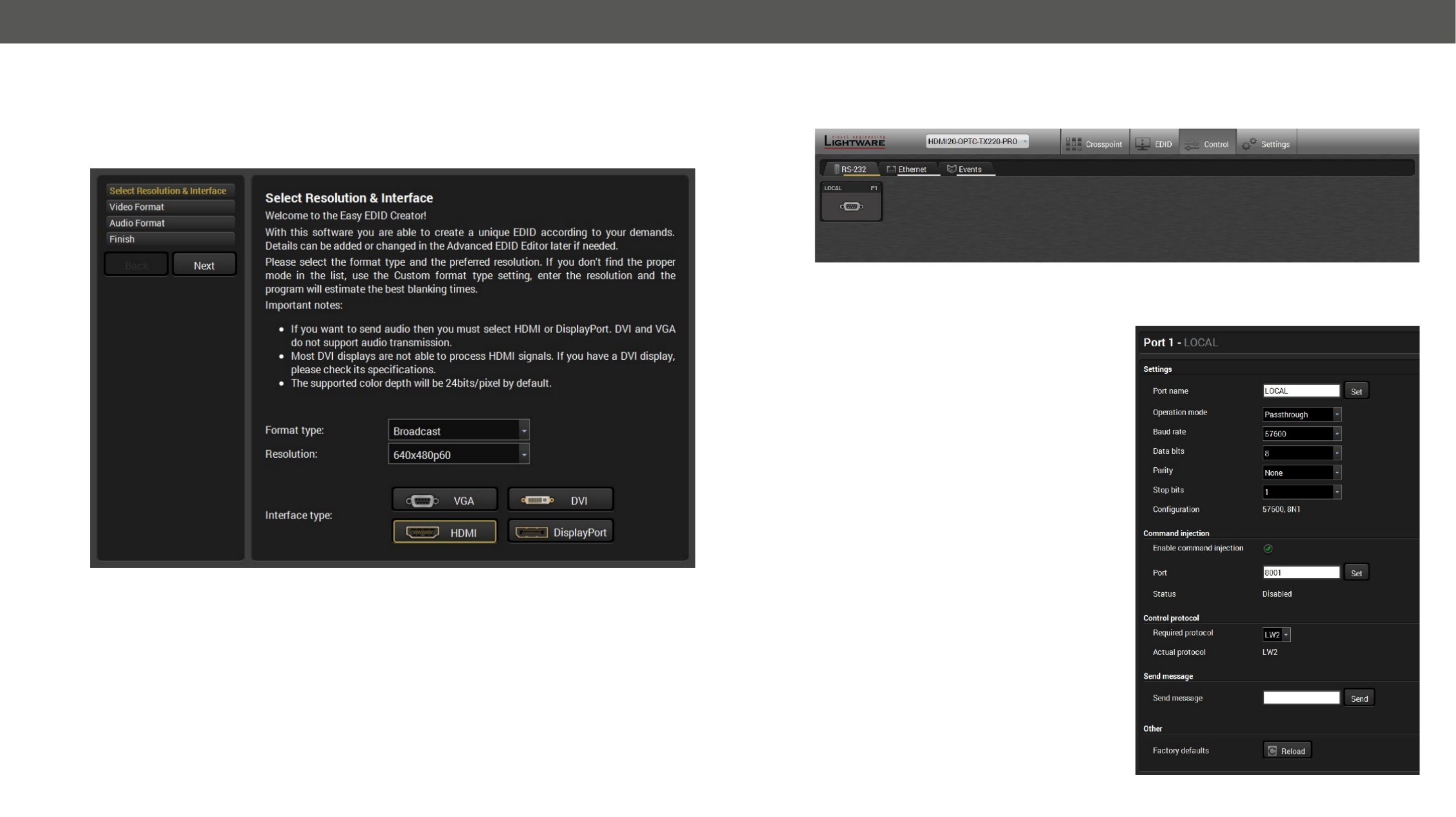
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 30
5.5.5. Creating an EDID
Since above mentioned Advanced EDID Editor needs more complex knowledge about EDID, Lightware
introduced a wizard-like interface for fast and easy EDID creation. With Easy EDID Creator it is possible to
create custom EDIDs in four simple steps. By clicking on the button below the left panel, Easy EDID Create
Creator is opened in a new window.
Easy EDID Creator Wizard
5.6. Control Menu
5.6.1. RS-232 Tab
RS-232 tab in Control menu
The following settings and functions are available on the local RS-232 port:
▪Port name
▪Operation mode: Pass-through, Control,
Command Injection, (for more details see Serial
Interface section);
▪Baud rate: 4800, 7200, 9600, 14400, 19200,
38400, 57600, 115200;
▪Data bits: 8 or 9;
▪Parity: None, Odd, or Even;
▪Stop bits: 1, 1.5, or 2;
▪Command injection: enable or disable;
▪Command injection port number;
▪Control protocol: LW2 or LW3;
▪Message sending via serial port;
▪Reloading factory defaults (see the Factory
Default Settings section).
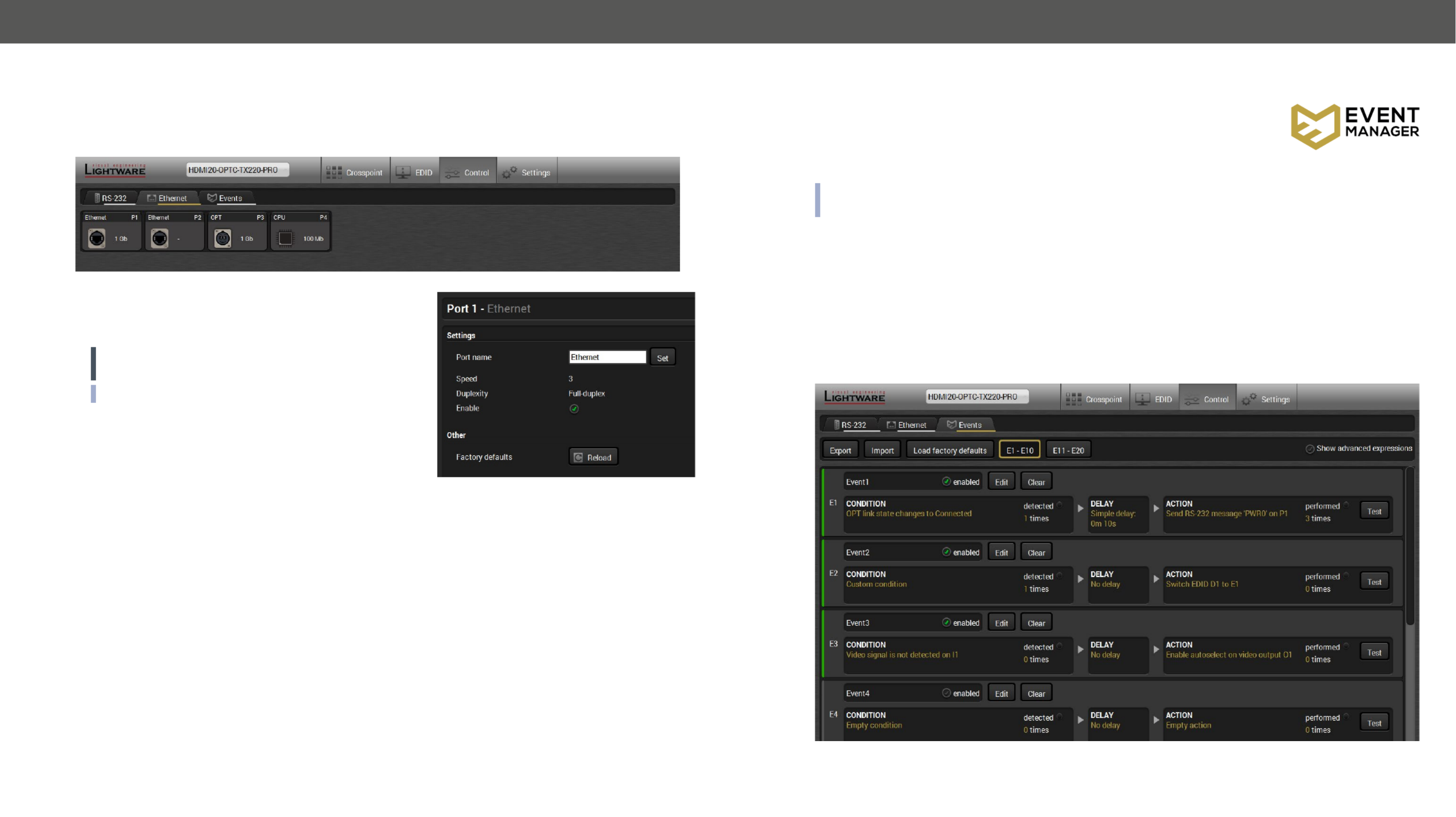
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 31
5.7. Event Manager
The feature means that the device can sense changes on its ports and able to
react according to the pre-dened settings. The development idea of the Event
manager is based on users’ feedbacks. In many cases internal events (such as
signal present) are necessary to display but it is not easy when the device is hard to
access (e.g. built under the desk).
INFO: For tips and tricks and detailed description about the application of Event Manager, please download
the Event Manager User's Guide from the Download section on the www.lightware.com.
The Event manager can be congured to perform an action if a condition has been detected. E.g. the desired
setup is that after a certain type of signal has been detected on I1 port, the port has to be switched to O1.
The settings can be done via the LDC in the Control/Events tab, or by LW3 protocol commands. Congurable
events number depends on the device what you are using actually.
Numerous new ideas and requests have been received in connection with the features and settings of the
Event manager since the rst release. Therefore, the user interface has been re-designed and many new
functions implemented. The Event editor can be opened by pressing the Edit button at each Event.
There is a on the left of the Event panel in each line. If a condition and an action are set and the Event gray bar
is enabled, the bar is displayed .in green
Control menu, Event Manager tab
5.6.2. Ethernet Tab
Four ports are displayed in the Ethernet tab: Ethernet (P1, P2), OPT1, and CPU. The Ethernet ports (P1 and
P2) display the status of the Ethernet, speed, and the duplexity of the connection. The following settings are
also available:
▪Enable / disable the port (for loop protection);
▪Reloading factory defaults (see factory default
settings in the Factory Default Settings section).
ATTENTION! If the Ethernet port is set to disabled, this
may break the connection with the device.
INFO: OPT1 and CPU Ethernet port can not be disabled.
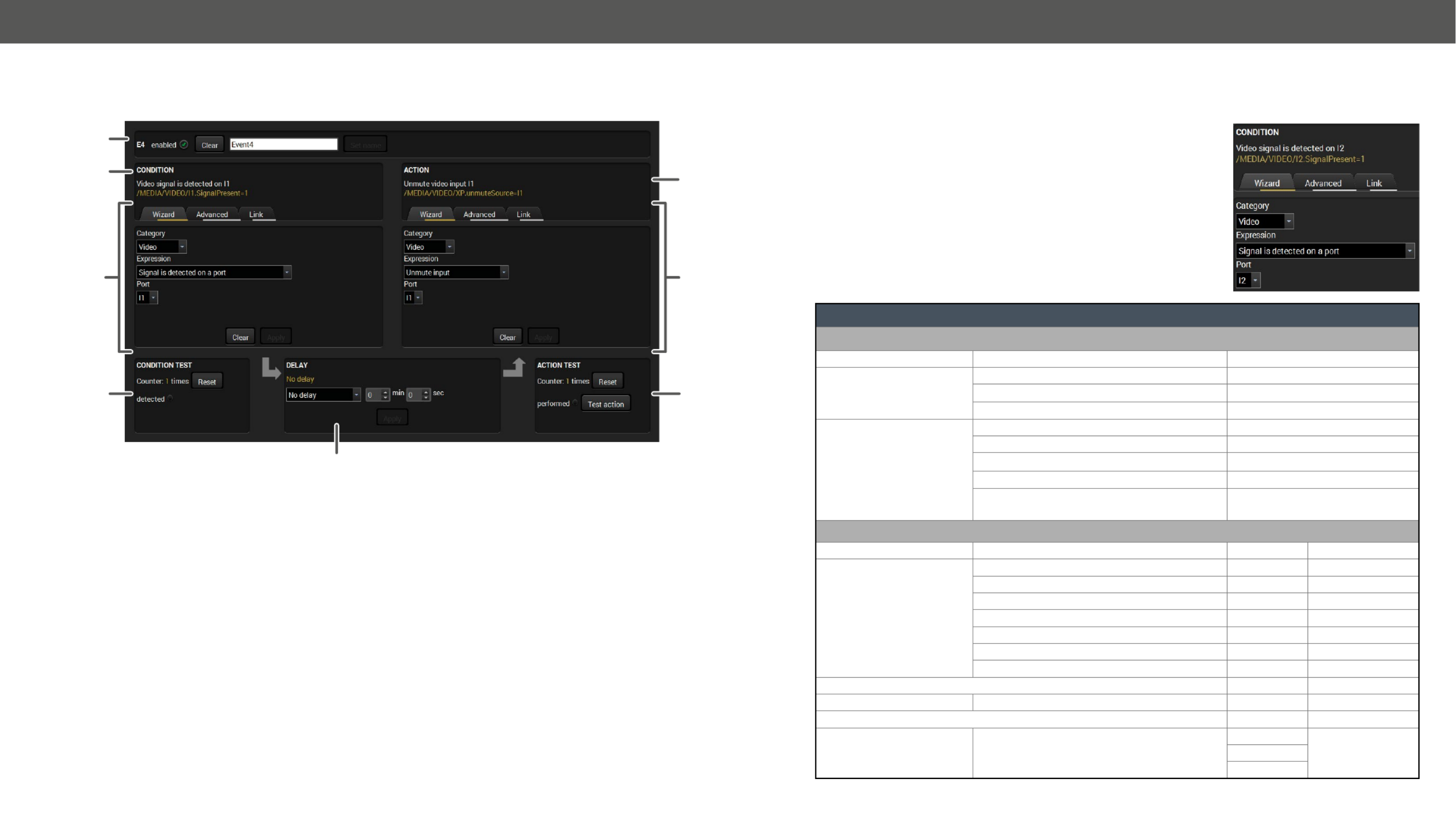
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 32
5.7.1. The Event Editor
Press the button in the desired Event line to open the Event editor window.Edit
7
1
2
4
5
6
8
3
1Event header The name of the Event is displayed. Type the desired name and press the Set
name button. The Event can be cleared by the Clear button. Use the tick mark
to enable/disable the Event.
2Condition header If the condition is set, the description (white colored text) and the exact LW3
protocol expression (yellow colored text) can be seen. If the advanced mode
was used the description is “Custom condition”.
3Condition panel The Wizard, the Advanced or the Link tool is available to set the condition.
The parameters and settings are displayed below the buttons.
4Condition test The set condition can be tested to see the working method in the practice.
5Delay settings The action can be scheduled to follow the condition after the set time value.
6Action header If the action is set, the description (white colored text) and the exact LW3
protocol expression (yellow colored text) can be seen. If the advanced mode
was used the description is “Custom action”.
7Action panel The Wizard, the Advanced or the Link tool is available to set the action. The
parameters and settings are displayed below the buttons.
8Action test The set action can be tested to see the working method in the practice.
5.7.2. Create or Modify an Event
Wizard Mode
The wizard mode lists the most common conditions and actions, so the
user does not have to look for LW3 nodes and properties.
Step 1. EditClick on the button of the desired Event; the is Event editor
displayed.
Step 2. The wizard mode is displayed as default. Select the desired
Category rst (e.g. Audio or Video).
Step 3. ExpressionSelect the desired from the drop-down menu. If any
other parameter is necessary to set, it is going to be displayed.
Step 4. ApplyPress the button to store the settings of the Condition.
Conditions and actions in wizard mode in the transmitter
Condition
Category Expression Ports
General
Select button is pressed
OPT link state changes to Connected
OPT link state changes to Disconnected
Video
Signal is detected on a port I1, I2, O1, O2
Signal is not detected on a port I1, I2, O1, O2
Signal type changes to DVI I1, I2, O1, O2
Signal type changes to HDMI I1, I2, O1, O2
Signal type changes to Undened (no
signal) I1, I2, O1, O2
Action
Category Expression Input Output
Video
Switch input to output I1, I2 O1, O2
Enable autoselect on output O1, O2
Disable autoselect on output O1, O2
Mute input I1, I2
Mute output O1, O2
Unmute input I1, I2
Unmute output O1, O2
Port Message
RS-232 Send RS-232 message P1
Source EDID Destination EDID
EDID Switch EDID
F1-146
E1, E2D1-2
U1-14
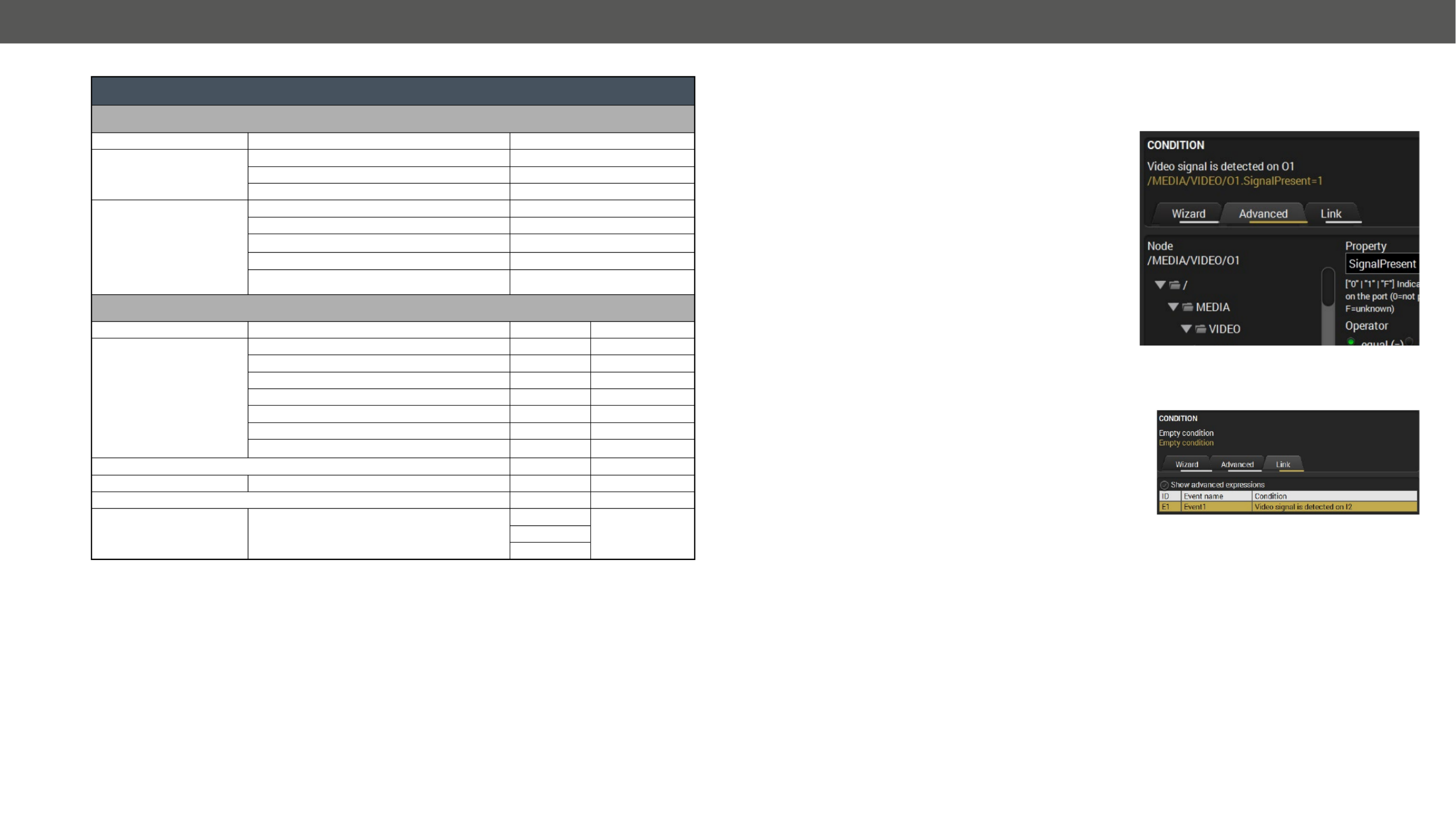
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 33
Conditions and actions in wizard mode in the receiver
Condition
Category Expression Ports
General
Function button is pressed
OPT link state changes to Connected
OPT link state changes to Disconnected
Video
Signal is detected on a port I1, O1, O2, O3
Signal is not detected on a port I1, O1, O2, O3
Signal type changes to DVI I1, O1, O2, O3
Signal type changes to HDMI I1, O1, O2, O3
Signal type changes to Undened (no signal) I1, O1, O2, O3
Action
Category Expression Input Output
Video
Switch input to output I1 O1, O2, O3
Enable autoselect on output O1, O2, O3
Disable autoselect on output O1, O2, O3
Mute input I1
Mute output O1, O2, O3
Unmute input I1
Unmute output O1, O2, O3
Port Message
RS-232 Send RS-232 message P1
Source EDID Destination EDID
EDID Switch EDID
F1-146
E1D1-2
U1-14
Advanced Mode
The goal of this mode is the same as of the wizard: set the properties and methods for conditions and
actions. The difference is the number of the available and usable properties and methods of the LW3
protocol. Advanced mode allows almost all of it.
Step 1. EditClick on the button of the desired Event; the
Event editor is displayed.
Step 2. The wizard mode is the default, press the
Advanced button. The LW3 protocol tree is
displayed showing the list of the properties in the
drop-down menu. Navigate to the desired node.
Step 3. PropertySelect the desired from the menu. The
manual of the property is displayed below to help
to select the necessary property and to set the
value.
Step 4. value operatorSet the desired and , then press the
Apply button to store settings.
The Link Tool
The interface allows creating more actions to the same condition. In that case, a condition can trigger more
actions. To set such an Event, the Link tool has been introduced.
Step 1. EditClick on the button of the desired Event; the
Event editor is displayed.
Step 2. The wizard mode is displayed as default, press the
Link button.
Step 3. All the saved Events are analyzed and the conditions
are listed (it takes some seconds to nish). The
Show advanced expressions option allows showing
the exact path and set the value of the given property.
Step 4. Condition ApplySelect the desired and press the button to store the settings.

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 34
5.7.3. Special Tools and Accessories
The Name of the Event
The name of a port can be changed by typing the new name and
clicking the button. The following characters are allowed Set name
when naming:
Letters (A-Z) and (a-z), numbers (0-9), special characters: hyphen ( - ),
underscore ( _ ), and space ( ).
Enable or Disable an Event
The set Event can be enabled or disabled in the Event list, or directly
in the Event editor window by setting the beside the name.tick mark
Testing the Condition
When the desired Condition is arranged, the setting can be tested. The
Event list and the Event editor contains a small panel that shows if
the set condition is detected and how many times. The can be Counter
reset by the button in Event editor. If the Condition is true, the detected
mark turns green for two seconds and the is increased.Counter
Testing the Action
The method is the same as testing the Condition, but in this case, the
Action can be triggered manually by pressing the Test button.
TIPS AND TRICKS: The Test button is also placed on the Action
panel in the Event list. Thus, you can check the Actions without
opening the Event editor.
Delay the Action
In most cases the Action is performed immediately after the Condition
is detected. But sometimes a delay is necessary between the Condition
and the Action. Therefore, the new Event manager contains the Delay
panel which allows that feature with below settings:
▪No delay: when the Condition is detected, the Action is launched.
▪Simple delay: when the Condition is detected, the Action is
launched after the set time interval.
▪Still exists: when the Condition is detected, the Action is launched
after the set time interval only if the Condition still exists.
▪Continuously exists: when the Condition is detected, the Action
is launched after the set time interval only if the Condition has
been existing continuously.
The Available Delay Settings of an Event
TIPS AND TRICKS: Show advanced expressions option is a useful
tool when you look for the path or value of a property but just the
expression is displayed. The option is available in the Event list
window or when Link tool is used.
5.7.4. Clear One or More Event(s)
Clear an Event
Press the button in the Event list or in the header section in the Clear
Event editor.
Clear all Events
When all the Events must be cleared press the Load factory defaults
button above the Event list. You will be prompted to conrm the
process.
5.7.5. Export and Import Events
The feature allows saving all the Events. The backup le can be
uploaded to the same device type.
Export all the Events
Step 1. Press the button above the Event list.Export
Step 2. The Save as dialog box will appear. Set the desired folder and
le name, then press the Save button.
The generated le is a simple text le which contains LW3 protocol
commands. The le can be viewed by a simple text editor, e.g. Notepad.
ATTENTION! Editing the le is recommended only for expert users.
Import all the Events
Step 1. Press the button above the Event list.Import
Step 2. The Open dialog box will appear. Select the desired folder and
le, then press the Open button.
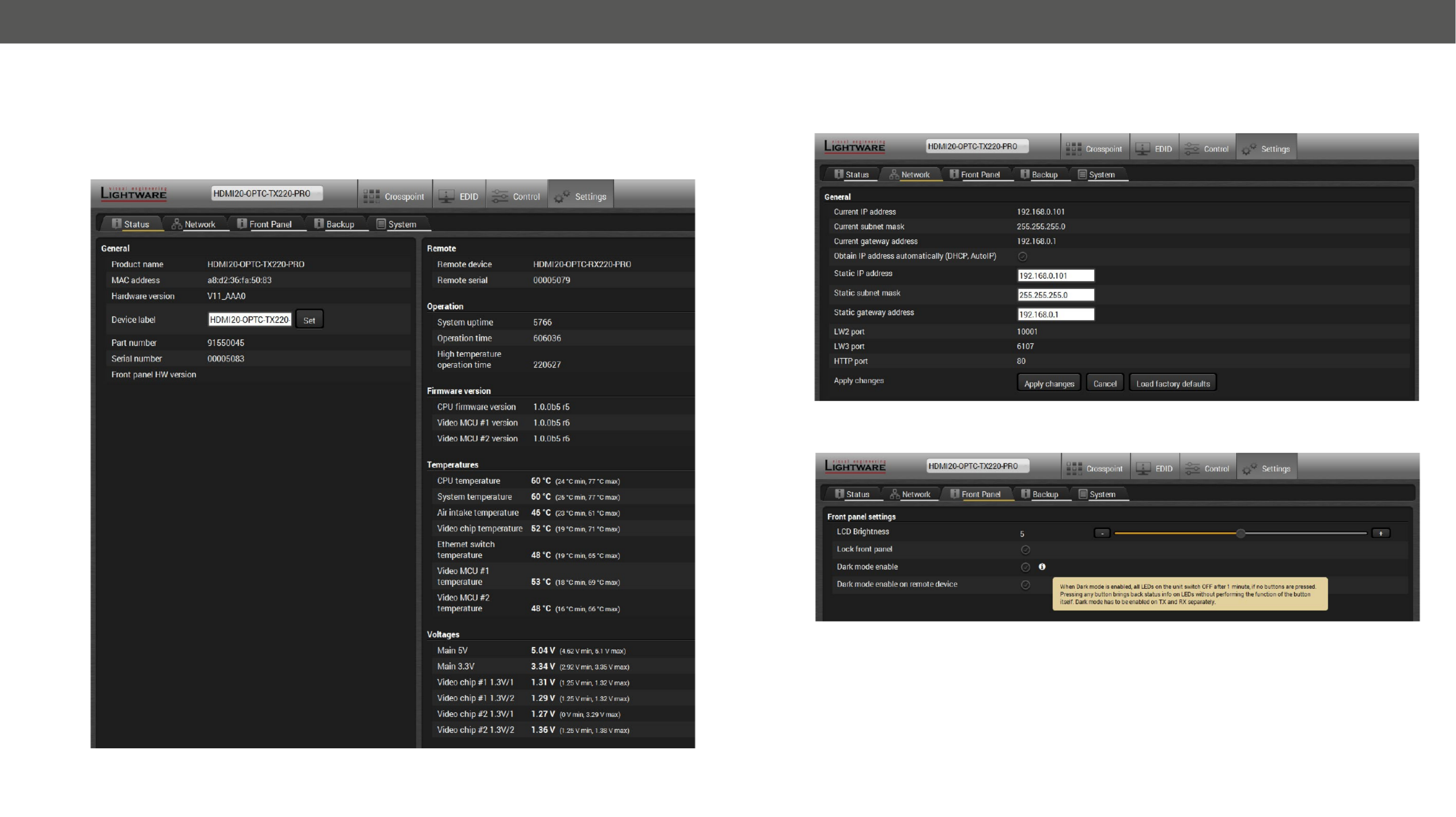
5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 35
5.8. Settings Menu
5.8.1. Status Tab
The most important hardware and software related information can be found on this tab: hardware and
rmware version, serial numbers, temperatures, operation time, voltage information, and fan status. Device
label can be changed to unique description by the button.Set
5.8.2. Network Tab
IP address and DHCP settings can be set on this tab. Always press the button to save changes. Apply changes
Factory default settings can be recalled with a dedicated button.
5.8.3. Front Panel Tab
Certain settings in connection with the front panel LCD are available in the LDC as well.
▪LCD brightness: the slider can be set from 0 to 10. When the value is 0, the LCD is totally dark.
▪Lock front panel: disables the control functions (button and jog dial knob) on the front panel.
▪Enable dark mode: enable/disable lighting of the LEDs on the front panel of transmitter. See more about
the dark mode in Front Panel Submenu section. The LEDs switch off after 60 s delay.
▪Enable dark mode on a remote device*: turn on/off the lighting of the LEDs on the front panel of the
receiver (which connected directly to the transmitter via ber).
*Remote setting of the dark mode is available only in the transmitter.

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 36
5.8.4. Backup Tab (Conguration Cloning)
Backup tab
The conguration cloning of Lightware LW3 devices is a simple method that eliminates the need to repeatedly
congure certain devices to have identical (non-factory) settings. If the devices are installed in the same type
of system multiple times then it is enough to set up only one device to t the user’s needs and then copy those
settings to the others, thus saving time and resources.
Cloning Steps in a Nutshell
Installing multiple devices with the same customized conguration settings can be done in a few easy steps:
Step 1. Congure one device with all your desired settings with the LDC software.
Step 2. Backup the full conguration le to your computer.
Step 3. If needed, make some modications to the conguration le using a text editor (e.g. Notepad). E.g.
modifying the static IP address is needed when DHCP is not used.
Step 4. Connect to the other device which has to be congured and upload (restore) your conguration le.
Step 5. Done! You can have as many totally identical, customized devices as you like.
Save the Settings of the Device (Backup)
Step 1. Apply the desired settings in the extender (port parameters, crosspoint, etc.)
Step 2. Settings BackupSelect the / tab from the menu.
Step 3. descriptionWrite a short in the text box on the left (optional).
Step 4. Press the Create a full backup button. You will be prompted to save the le to the computer. The default
le name is the following:
BACKUP_<DEVICE TYPE>_SN<SERIAL NUMBER>.LW3
Step 5. saveSet the desired , select the folder and le name the le.
TIPS AND TRICKS: Using the exact product type in the lename is recommended since it makes the le
usage more comfortable.
About the Backup File
The backup le is a simple text le which contains LW3 protocol commands. The rst line is the description,
and the further lines are the commands which will be executed during the restore process. The le can be
viewed (and/or edited) by a simple text editor, e.g. Notepad.
ATTENTION! Editing the command lines is only recommended for expert users.
Upload the Settings to a Device (Restore)
WARNING! Please note that the settings will be permanently overwritten with the restored parameters
in the device. Withdrawal is not possible.
ATTENTION! The cloning is successful when the backup le is downloaded from the same type of source
device as the destination device.
The Restoring Process
Step 1. Settings BackupSelect the / tab from the menu.
Step 2. browseClick on the button on the right panel and Choose le the desired le.
Step 3. The le is checked and the result will be displayed in the textbox below. If the le is correct, the
settings can be restored.
Step 4. Choose IP settings what you want to use after backup. You can apply settings from the backup le,
keep actual settings, set it manually in a dialog box or apply DHCP.
Step 5. Start restore processPress the button and click on the Yes button when asked.

5. Software Control – Using Lightware Device Controller HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 37
Create and Restore Backups from the Device Memory
HDMI20-OPTC series extenders are able to store backups in their own memory and these can be recalled
from there so user does not need to save backup les to the local computer. Four slots are available for this
purpose.
You can save presets as not protected with using button and as protected with using the Save Save as protected
button. To restore a preset select the slot of the desired backup and click on the button. You can save Apply
presets from a le from your local computer by clicking on the Upload button and you can also save a preset
from the device's memory to a backup le with using the Download button. If you do not need a saved preset
any more, select it and click on the button.Delete
WARNING! Loading factory default settings will erase not protected presets which have been saved in
the device memory!
5.8.5. System
Three functions are available under System tab:
▪Download system log - saving the log le of the device.
INFO: In case of the troubleshooting process, this log le can help the support localize the problem.
▪Load factory defaults - recalling factory defaults settings and values. All factory default settings are
listed in the Factory Default Settings section.
▪Reboot - rebooting the system.
5.9. Advanced View Window
1LW3 protocol help Pushing the button results a help window opening which describes the most
important information about LW3 protocol commands in HTML format.
2Edit mode The default appearance is the read-only mode. If you want to modify the values or
parameters, tick the option. You will be prompted to conrm your selection.
3Warning mode If this pipe checked in, a warning window pops up when you enable Edit mode.
4Terminal window Commands and responses with time and date are listed in this window. Sent
command starts with ‘>’ character, received response starts with ‘<’ character.
The color of each item depends on the type of the command and response. The
content of the window can be emptied by the button. If the Clear Autoscroll option
is ticked, the list is scrolled automatically when a new line is added.
5Command line Type the desired command and execute it by the button. .Send
6Protocol tree LW3 protocol tree; select an item to see its content.
7Node list Correspondent parameters and nodes are shown which are connected to the
selected item in the protocol tree.
Manual button: Manual (short description) of the node can be called and
displayed in the terminal window.
Set button: Saves the value/parameter typed in the textbox.
Call button: Calls the method, e.g. reloads factory default settings.
12 3
4
5
6
7

HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 38
6.1. Overview
different products with a different feature list.
All commands are terminated with a carriage return (Cr, ‘\r’) and line feed (Lf, ‘\n’) pair. In order to implement
scalability and sustainability, we decided to organize all settings, parameters and properties of the device to
a tree structure with and .nodes, properties, methods
6.1.1. Elements of the Tree Structure
ATTENTION! All names and values are case-sensitive. The space character is replaced by the ‘ ’ character ●
in the elements and commands descriptions.
6.1.1.1. Node
▪ The basic building block of the tree structure is the ‘node’.
▪ The node can have multiple child nodes, but only one parent.
▪ The tree has only one root the ‘root node’.
▪ The leaves of the tree are also nodes, which do not have child nodes.
▪
▪ All the slashes are ‘right slashes’, no backslash is used.
▪
▪ The node name can contain the elements of the English alphabet and numbers.
▪ Recommended convention for case sensitivity:
– Fix nodes (that cannot be altered) are capitalized.
– User created nodes can contain both lowercase and capital letters, no restrictions.
▪ The path of a node has to contain all parent nodes from the root node.
●
●
Legend:
n: node
‘-’: default for a node.
‘m’: this is a manual for the node.
‘E’: this is an error message for the node.
's': this is a symlink node.
'v': this node has virtual children.
'r': this is a remote node.
INFO: All parent nodes must be listed in the path of a node.
6
LW3 Programmers’ Reference
The device can be controlled through Lightware 3 (LW3) protocol commands to ensure the compatibility with other
Lightware products. The supported LW3 commands are described in this chapter.
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 39
Following example presents the structure of the tree traversal:
Tree structure of the nodes
6.1.1.2. Property
The ‘property’ in the LW3 protocol is basically a leaf, which has a well-dened value.
▪ A property has a value.
▪ A property cannot have child nodes or child properties. It is always a leaf.
▪ A node can have any number of properties (may not have any).
▪ A property is referenced with a dot (‘.’) after the node name.
▪ The properties’ name can contain the elements of the English alphabet, numbers and underscore (‘_’)
character.
▪ By convention, properties are beginning with a capital letter, all other characters are lowercase ones.
In the case of compound words, all words are beginning with a capital letter (CamelCase).
▪ The value of the property can contain any readable ASCII character.
▪ A property can be read-only or read/write.
Format: pX /[nodeName].[propertyName]=[propertyValue]●
Legend:
p: property
‘X’ can be:
‘r’: if the property is read-only.
‘w’: if the property is readable, writable.
‘m’: the manual of the property.
‘E’: error message for the property.
'v': virtual node property: contains a node path to a node which will
be linked to the property's parent node.
node2
node3
node1n-/
node12
node21
node11
node211
Path of the nodes:
n- /node1
n- /node1/node11
n- /node1/node12
n- /node2
n- /node2/node21
n- /node2/node21/node211
n- /node3
Example:
The following two ones are read-only properties:
pr●/node1/node12.ReadOnlyProperty=value1
pr●/.ProductName=HDMI20-OPTC-TX22
The following two ones are read-write properties:
pw●/node1/node12.ReadWriteProperty=value2
pw●/.DeviceNickName=John
6.1.1.3. Method
The ‘method’ in the LW3 protocol is also a leaf. It cannot have a value, such as the properties, but it can be
invoked with a parameter with the help of a special ‘CALL’ command.
▪ A method cannot have child nodes or child methods. It is always a leaf.
▪ A node can have any number of methods (may not have any).
▪ A method is referenced with a colon (‘:’) after the node.
▪ The methods’ name can contain the elements of the English alphabet, numbers and underscore (‘_’)
character.
▪ By convention, methods are beginning with a lowercase letter. In the case of compound words, the
very rst letter is lowercase, and the rst letter of each other words are capitalized (lowerCamelCase).
▪ The parameter of the method can contain any readable ASCII character.
▪ The method always has a return ‘state’ if the method could be executed. The state could be either ‘OK’
or ‘FAILED’.
▪ The method does not necessarily have a return ‘value’. If it does, it can contain additional information,
which is always specic to the current case (the return value can specify why the execution failed).
▪ When the method cannot be executed (e.g. the parameter list is illegal), there is an error message.
Format: mX /[nodeName]:[methodName]=[returnValue]●
Legend:
m: method
‘X’ can be:
‘O’: when the execution of the method was successful (OK).
‘F’: when the execution of the method failed.
‘m’: the manual of the method.
‘E’: error message for the method.
Example:
mO●/node1/node12:method1
mO●/MEDIA/XP/VIDEO:switch
mE %E001:Syntax error●
mm●/MEDIA/XP/VIDEO:lockSource:Lock one or more source ports

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 40
6.1.2. Escaping
Property values and method parameters can contain characters that are used as control characters in the
protocol. They must be escaped. The escape character is the backslash (‘\’) and escaping means injecting
a backslash before the character that should be escaped (like in C language).
Control characters are the followings: \ { } # % ( ) \r \n \t
Example:
The original text: John (Doe). node1\node11● ● ● ●#3: 5%2=1
The escaped text: John \(Doe\). node1\\node11● ● ● ●\#3: 5\%2=1
6.1.3. Error Messages
There are several error messages dened in the LW3 protocol, all of them have a unique error number.
Format: XE● ● ●[primitive] %EYYY: [Error message]
Legend:
‘X’ can be:
‘-’: syntax error. Cannot parse the command at all.
‘n’: node error.
‘p’: property error.
‘m’: method error.
YYY: error code, which can be one of the followings:
Error code Name Default text
000 Lw3ErrorCodes_None
001 Lw3ErrorCodes_Syntax Syntax error
002 Lw3ErrorCodes_NotFound Not found
003 Lw3ErrorCodes_AlreadyExists Already exists
004 Lw3ErrorCodes_InvalidValue Invalid value
005 Lw3ErrorCodes_IllegalParamCount Illegal parameter count
006 Lw3ErrorCodes_IllegalOperation Illegal operation
007 Lw3ErrorCodes_AccessDenied Access denied
008 Lw3ErrorCodes_Timeout Timeout
009 Lw3ErrorCodes_CommandTooLong Command too long
010 Lw3ErrorCodes_InternalError Internal error
011 Lw3ErrorCodes_NotImplemented Not implemented
012 Lw3ErrorCodes_Node_Disabled Node disabled or standby mode active
6.1.4. Prex Summary
The following prexes are dened in the LW3 protocol:
‘n-’: a node,
‘nE’: an error for a node,
‘nm’: a manual for a node,
‘pr’: a read-only property,
‘pw’: read-write property,
‘pE’: an error for the property,
‘pm’: a manual for the property,
‘m-’: a method,
‘mO’: a response to a success method execution,
‘mF’: a response to a failed method execution,
‘mE’: an error for a method,
‘mm’: a manual for a method.
6.2. The Tree Structure
The /MEDIA node is used by the LDC to connect input ports
to output ports on different layers. Each subnode of /MEDIA
is representing a layer, e.g. video (/MEDIA/ VIDEO), RS-232 (/
MEDIA/ UART) or Ethernet(/MEDIA/ ETHERNET). Each layer
has a crosspoint to dene connections between the ports
associated with the layer, all of them are represented by a
specic node. E.g. the video layer node is /MEDIA/VIDEO:
under the video layer node, the video crosspoint node (XP) and
the video ports (I1, O1, …) are located. The /SYS node is used
for system-related settings such as front panel settings and
health status parameters. The /MANAGEMENT node contains
network-related parameters, date-time settings, and version
numbers. The /EDID node contains all EDID-related settings
such as factory pre-programmed EDIDs and User EDIDs. All
input and output port settings, crosspoint state, etc... are under
the /MEDIA node.
INFO: The tree structure is available in the of LDC.Advanced View Window
MANAGEMENT
MEDIA
EDID
SYS
/
ETHERNET
UART
VIDEO
PRESETS
REMOTE
EVENTS

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 41
6.3. LW3 Commands
6.3.1. Get Command
The ‘GET’ command can be used to get the child nodes, properties and methods of a specic node. It can
also be used to get the value of a property.
The response format
The rst two characters of a response unambiguously identify the type of the element that the response
line concerns. The rst character is the type of the element (node, property or method), the second is for
miscellaneous information (e.g. read/write rights).
The dened prexes are:
‘n-’: node
‘pr’: property - only readable
‘pw’: property - writable, readable
‘m-’: method executable
After the prex, the response contains the full path of the node, property or method after a space character.
Get all children of a node
Get all of the child nodes of a parent node, with one GET command.
Command format: GET [nodePath]●
Response format: n-●[nodePath]
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA
˂n- /MEDIA/VIDEO
˂n- /MEDIA/UART
˂n- /MEDIA/ETHERNET
Get all child nodes, properties and methods of a node
Get all child nodes, properties and methods of a node with one command, without using a wild card.
Command format: GETALL [nodePath]●
Response format: (for nodes)
n- [nodePath]●
Response format: (for properties)
pX [nodePath].[propertyName]=[parameter]●
Legend:
X can be:
‘r’: read-only
‘w’: read-write
Response format: (for methods)
m- [nodePath]:[methodName]●
Example:
˃GETALL /EDID
˂n- /EDID/F
˂n- /EDID/D
˂n- /EDID/U
˂n- /EDID/E
˂pr /EDID.EdidStatus=D1:E1;D1:E2
˂m- /EDID:copy
˂m- /EDID:delete
˂m- /EDID:reset
˂m- /EDID:switch
˂m- /EDID:switchAll
Get all properties and methods of a node
Get all properties and methods of a node, with one GET command and asterisk character.
Command format: GET [nodePath].*●
Response format: (for properties)
pX [nodePath].[propertyName]=[parameter]●
Legend:
X can be:
‘r’: read-only
‘w’: read-write
Response format: (for methods)
m- [nodePath]:[methodName]●

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 42
Example:
˃GET /EDID.*
˂pr /EDID.EdidStatus=D1:E1;D1:E2
˂m- /EDID:copy
˂m- /EDID:delete
˂m- /EDID:reset
˂m- /EDID:switch
˂m- /EDID:switchAll
6.3.2. Set Command
The setter command can be used to modify the value of a property.
Command format: SET●[nodePath].[propertyName]=[newPropertyValue]
Response format:
The response for setting a property to a new value is the same as the response for the ‘GET’ command. The
value in the response is the new value if the execution of the ‘SET’ command was successful, otherwise the
unmodied ‘old value’ with an error message.
pw●[nodePath].[propertyName]=[newPropertyValue]
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=false
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=false
˂CHG /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=false
Error Response format:
If there were errors during setting a property, an error message follows the unmodied property value.
pE● ●[nodePath].[propertyName]=[umodiedValue] %EXXX:Error message
Legend: XXX: error number.
Examples:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.CommandInjectionEnable=2
˂pE /MEDIA/UART/P1.CommandInjectionEnable %E004:Invalid value
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask=255.255.255.5
˂pE /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask %E007:Access denied
6.3.3. Invocation
A method can be invoked with the help of the ‘CALL’ command.
Command format: CALL [nodePath]:[methodName]([parameter])●
Response format:
The response for a method execution is a state and a value. The state is mandatory and always dened if
the method could be executed. It can be either a success or a failure. The value is optional and it can contain
additional information, such as the reason why the state is a failure or a specic value when the state is
a success that the client can process. It is also possible to get an error message when the method could
not be executed – e.g. the parameter was illegal - and hence not even the state of the execution could be
specied.
mX [nodePath]:[methodName]=Y●
Legend:
X can be:
‘O’: if the execution is successful.
‘F’: if the execution is failed, but the method could be executed.
‘E’: if the method could not be executed: e.g. illegal parameter count.
Y can be:
▪ The return value of the method if any.
▪ It is valid that a method does not have any return value. In this case, the equal sign
(‘=‘) can be omitted.
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:switch(D1:E1)
˂mO /EDID:switch
Error Response format:
If there were errors during the execution, an error message is received, which follows the method name.
mE [nodePath]:[methodName]● ●%EXXX:Error message
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:switch(D1:R1)
˂mE /EDID:switch %E004: Invalid value
6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 43
6.3.4. Manual
For every node, property and method in the tree there is a manual. The manual is a human-readable text that
describes the syntax and provides a hint for how to use the primitives.
Command format:
for nodes: MAN [nodePath]●
for property: MAN [nodePath].[propertyName]●
for method: MAN [nodePath]:[methodName]●
Response format:
The human readable manual is separated by a space (‘ ‘) character from the primitives.
for nodes: nm [nodePath] Human readable manual● ●
for property: pm [nodePath].[propertyName] Human readable manual● ●
for method: mm [nodePath]:[methodName] Human readable manual● ●
Example: (for a property)
˃MAN /MEDIA/UART/P1.Baudrate
˂pm /MEDIA/UART/P1.Baudrate [<id_of_baudrate>] Baud rate (0=4800; 1=7200; 2=9600;
3=14400; 4=19200; 5=38400; 6=57600; 7=115200)
Example: (for a method)
˃MAN /SYS:factoryDefaults
˂mm /SYS:factoryDefaults [] Restart the device and set all the settings to factory
default
6.3.5. Signature
For some command, the response can contain multiple lines. Each line is terminated with a carriage return
(Cr, ‘\r’) and line feed (Lf, ‘\n’) characters. In several cases the number of the lines in the response cannot
be determined in advance, e.g. the client is intended waiting for the whole response and also wants to be
sure, that the received lines belong together and to the same command. In these cases, a special feature the
‘signature’ can be used.
The signature is a four digit long hexadecimal value that can be optionally placed before every command.
In that case, the response to that particular command will also be preceded by the signature, and the
corresponding lines will be between brackets.
Command format: XXXX#[command]
Legend: xxxx: 4-digit long hexadecimal value.
Response format:
{XXXX
[command lines]
}
Example:
˃1103#GET /MEDIA/VIDEO.*
˂{1103
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.PortCount=4
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.PortUi=O1:02003;O2:03003;I1:01021;O3:04003
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.O1=HDMIOUT1A
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.O2=HDMIOUT1B
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.I1=OPTIN
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO.O3=HDMIOUT2
˂}
INFO: The lines of the signature are also Cr and Lf terminated.
6.3.6. Subscription
The user can subscribe to any node. Subscribe to a node means that the user will get a notication if any of
the properties of the node is changed. These notications are asynchronous messages - such as the ones
described above - and hence, they are useful to keep the client application up-to-date, without receiving any
unwanted information. When the user does not want to be informed about the changes anymore, he can
simply unsubscribe from the node.
ATTENTION! The subscriptions are handled separately for connections. Hence, if the connection is
terminated all registered subscriptions are deleted. After closing a connection the subscribe command
has to be sent in order to get the notications of the changes on that connection.
Subscribe to a node
Command format: OPEN [nodePath]●
Response format: o-●[nodePath]
Example:
˃OPEN /MEDIA/VIDEO
˂o- /MEDIA/VIDEO
Subscribe to multiple nodes
In order to subscribe to multiple nodes, the asterisk wild card can be used.
Command format: OPEN●[nodePath]/*
Response format: o-●[nodePath]/*
Example:
˃OPEN /MEDIA/VIDEO/*
˂o- /MEDIA/VIDEO/*
6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 44
Get the active subscriptions for the current connection
Command format: OPEN
Response format: o- [nodePath]●
Example:
˃OPEN
˂o- /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP
˂os /MEDIA/VIDEO/I1
˂os /MEDIA/VIDEO/I2
˂o- /MEDIA/VIDEO
˂os /REMOTE/D1
˂o- /MANAGEMENT/UID
˂o- /
Unsubscribe from a node
Command format: CLOSE [nodePath]●
Response format: c- [nodePath]●
Example:
˃CLOSE /MEDIA/VIDEO
˂c- /MEDIA/VIDEO
Unsubscribe from multiple nodes
Command format: CLOSE●[nodePath]/*
Response format: c-●[nodePath]/*
Example:
˃CLOSE /MEDIA/VIDEO/*
˂c- /MEDIA/VIDEO/*
6.3.7. Notications about the Changes of the Properties
When the value of a property is changed and the user is subscribed to the node, which the property belongs
to, an asynchronous notication is generated. This is notication is called as the ‘change message’. The
format of such a message is very similar to the response for the ‘GET’ command.
Format: CHG●[nodePath].[propertyName]=[newPropertyValue]
Example:
˂CHG /MEDIA/VIDEO/O1.ForcedSignalType=HDMI
A short example of how to use the subscription
In the following, an example is presented, how the subscriptions are working and how to use them. In the
example, there are two independent users controlling the device through two independent connections
(‘Connection #1’ and ‘Connection #2’). The events in the rows occur after each other.
Conn. #1
˃OPEN /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP
˂o- /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList=I1;I1
Conn. #2
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList=I1;I1
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch(I2:O1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch
Conn. #1 ˂CHG /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList=I2;I2
Explanation: The rst user (Connection #1) set a subscription to a node. Later the other user (Connection
#2) made a change, and thanks for the subscription, the rst user got a notication about the change.
6.4. Formal Denitions
Method parameters and property values are specied in a modied version of Backus-Naur Form (BNF). The
syntax is the following:
“literal” literals are quoted
<expression1>|<expression2> vertical bars denote alternatives
[<expression>] expressions in square brackets are optional
<number>*[<expression>] expression is repeated at least <number> times
*[<expression>] <number> may be omitted, in this case number defaults to 0
<number>*{<expression>} expressions in curly brackets are repeated exactly <number>
times
In Input port number
Om Output port number

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 45
6.5. System Commands
6.5.1. Querying the Product Name
The name of the product is a read-only parameter and cannot be modied.
Command format: GET●/.ProductName
Response format: pr●/.ProductName=<Product_name>
Example:
˃GET /.ProductName
˂pr /.ProductName=HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-PRO
6.5.2. Setting the Device Label
ATTENTION! The device label can be changed to a custom text which is displayed in many windows of
the LDC. This writable parameter is not the same as the ProductName parameter.
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/UID/DeviceLabel=<Custom_name>
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/UID/DeviceLabel=<Custom_name>
The Device Label can be 39 character length and ASCII characters are allowed. Longer names are truncated.
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/UID.DeviceLabel=HDM20-OPTC_Control_room
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/UID.DeviceLabel=HDM20-OPTC_Control_room
6.5.3. Querying the Serial Number
Command format: GET●/.SerialNumber
Response format: pr●/.SerialNumber=<serial_nr>
Example:
˃GET /.SerialNumber
˂pr /.SerialNumber=92345083
6.5.4. Querying the Firmware Version
Command format: GET●/SYS/MB.FirmwareVersion
Response format: pr●/SYS/MB.FirmwareVersion=<rmware_version>
Example:
˃GET /SYS/MB.FirmwareVersion
˂pr /SYS/MB.FirmwareVersion=1.0.0b9 r9
6.5.5. Resetting the Extender
The extender can be restarted – the current connections (LAN, RS-232) will be terminated.
Command format: CALL●/SYS:reset()
Response format: mO●/SYS:reset=
Example:
˃CALL /SYS:reset()
˂mO /SYS:reset=
6.5.6. Restoring the Factory Default Settings
Command format: CALL●/SYS:factoryDefaults()
Response format: mO●/SYS:factoryDefaults=
Example:
˃CALL /SYS:factoryDefaults()
˂mO /SYS:factoryDefaults=
6.5.7. Locking Front Panel
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/UI.ControlLock=0|1|2
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/UI.ControlLock=0|1|2
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/UI.ControlLock=1
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/UI.ControlLock=1
Legend:
▪ 0: None - All functions of the front panel button are enabled.
▪ 1: Locked - The front panel button is locked.
▪ 2: Force Locked - The front panel button is locked and unlock is only possible via protocol command.
6.5.8. Enabling Dark Mode
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/UI.DARKMODE.DarkModeEnable=true|false
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/UI.DARKMODE.DarkModeEnable=true|false
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeEnable=true
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeEnable=true
Explanation: The LEDs and the brightness of LCD display on the extender are turned off.

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 46
6.5.9. Setting the Dark Mode Delay
The LEDs turn off after the dark mode is enabled. The delay time can be set (the default value is 60s).
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/UI.DARKMODE.DarkModeDelay=<delay_sec>
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/UI.DARKMODE.DarkModeDelay=<delay_sec>
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeDelay=10
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeDelay=10
Explanation: When dark mode is enabled, the LEDs are turned off after 10s.
6.5.10. Setting the Dark Mode on the Remote Device
INFO: This command is available for HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro model.
Dark mode on the receiver can be activated by sending a command to the transmitter.
Command format: SET●/REMOTE/D1.DarkModeEnable=true|false
Response format: pw●/REMOTE/D1.DarkModeEnable=true|false
Example:
˃SET /REMOTE/D1.DarkModeEnable=true
˂pw /REMOTE/D1.DarkModeEnable=true
Explanation: LEDs on the receiver are turned off.
6.5.11. Setting the Rotary Direction of the Jog Dial Knob
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/UI.RotaryDirection=0|1
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/UI.RotaryDirection=0|1
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/UI.RotaryDirection=0
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/UI.RotaryDirection=0
Legend:
▪ 0: The rotary direction of down is clockwise.
▪ 1: The rotary direction of down is counter clockwise.
6.6. Video Port and Crosspoint Settings
6.6.1. Querying the Crosspoint Setting
Command format: GET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList
Response format: pr●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList=<O1_state>;<O2_state>
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList=I1;I1
Explanation: I1 input port is connected to all output ports.
6.6.2. Switching Video Input
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch(<In>:<Om>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch(I1:O1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 47
6.6.3. Querying the Status of Source Ports
Command format: GET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.SourcePortStatus
Response format: pr●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.SourcePortStatus=[<I 1><I
2>]
The response contains 5 ASCII characters for each port. The rst character indicates the mute/lock state,
the next four characters represent a 2-byte HEX code showing the current state of the input ports.
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.SourcePortStatus
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.SourcePortStatus=T008F;T008A
Legend:
Example and Explanation (T008F):
T 0 0 8 F
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 00 1 1 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio Unknown Signal
presents Connected
Letter (Character 1)
Mute state Lock state
TUnmuted Unlocked
LUnmuted Locked
MMuted Unlocked
UMuted Locked
Byte 1 Byte 2
Character 2 Character 3 Character 4 Character 5
BIT 7-6 BIT 5-4 BIT 3-2 BIT 1-0 BIT 7-6 BIT 5-4 BIT 3-2 BIT 1-0
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Embedded
audio status HDCP status
Signal
present
status
Connection
status
0 0
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
Unknown
0 1 Reserved
1 0
No
embedded
audio
Not
encrypted No signal Not
connected
1 1
Embedded
audio
presents
Encrypted Signal
presents Connected
T 0 0 E F
Mute / Lock status
Reserved character, always 0.
Reserved character, always 0.
Embedded audio / HDCP status
Signal present / Connection status
Letter
Byte 1
Byte 2
The Most Common Received Port Status Responses
T00AA
T 0 0 A A
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio
Not
encrypted No signal Not
connected
T00AB
T 0 0 A B
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio
Not
encrypted No signal Connected
T00AF
T 0 0 A F
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio
Not
encrypted
Signal
presents Connected
T00EF
T 0 0 E F
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Embedded
audio presents
Not
encrypted
Signal
presents Connected
T00BF
T 0 0 B F
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio Encrypted Signal
presents Connected
T00FF
T 0 0 F F
Unlocked,
Unmuted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Embedded
audio presents Encrypted Signal
presents Connected

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 48
6.6.4. Querying the Status of Destination Ports
Command format: GET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortStatus
Response format: pr●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortStatus=[<O 1><O2>]
The response contains 5 ASCII characters for each port. The rst character indicates the mute/lock state,
the next 2-byte long HEX code showing the current state of the output port.
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortStatus
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortStatus=T008E;M008E
Legend: See at previous section.
Example:
M 0 0 8 E
Unlocked,
Muted
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 00 1 1 10
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved No embedded
audio Unknown Signal
presents Connected
6.6.5. Muting Input Port
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:muteSource(<I n>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:muteSource
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:muteSource(I1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:muteSource
6.6.6. Unmuting Input Port
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unmuteSource(<I n>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unmuteSource
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unmuteSource(I1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unmuteSource
6.6.7. Locking Input Port
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:lockSource(<I n>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:lockSource
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:lockSource(I1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:lockSource
6.6.8. Unlocking Input Port
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unlockSource(<I n>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unlockSource
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unlockSource(I1)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unlockSource
6.6.9. Querying the Video Autoselect Settings
Command format: GET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortAutoselect
Response format: pr●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortAutoselect=<O 1_set>; <O2_set>
The response shows the settings of output1 and output2.
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortAutoselect
˂pr /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortAutoselect=EP;EP
Legend:
Letter Explanation
1st letter E: Autoselect is enabled.
D: Autoselect is disabled.
2st letter
F: First detect mode: the rst active video input is selected.
P: Priority detect mode: always the highest priority active video input will be selected.
L: Last detect mode: always the last attached input is switched to the output
automatically.
Explanation:
EP: the Autoselect is Enabled on output 1 and output 2, selected mode is Priority detect.

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 49
6.6.10. Changing the Autoselect Mode
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselect(<O n>:<On_set>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.setDestinationPortAutoselect
Example1:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselect(O2:D)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselect
Legend: See the previous legend.
Explanation: D: the Autoselect is disabled on output 2.
Example2:
˃CALL /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselect(O1:EF)
˂mO /MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselect
Legend: See previous legend.
Explanation: EF: First priority detect is set on output 1.
6.6.11. HDCP Setting
This setting allows to send non-encrypted content to a non-HDCP compliant display. See more information
in section.HDCP Management
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/<In>.HdcpVersion=0|1|2
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/VIDEO/<In>.HdcpVersion=0|1|2
Legend:
Value Description
0 Disable HDCP on input
1 Allow HDCP 1.4 only
2 Allow HDCP 2.2 and HDCP 1.4
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/VIDEO/I1.HdcpVersion=0
˂pw /MEDIA/VIDEO/I1.HdcpVersion=0
6.6.12. Setting the Output Conversion Mode
INFO: This command is available on the O1 output of HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro model.
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/VIDEO/O1.Conversion=OFF|420|LEFT|RIGHT
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/VIDEO/O1.Conversion=OFF|420|LEFT|RIGHT
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/VIDEO/O1.Conversion=420
˂pw /MEDIA/VIDEO/O1.Conversion=420
Legend:
▪ OFF: No conversion mode (transparent)
▪ 420: Converts to YCbCr 4:2:0
▪ LEFT: Split mode, output on the left side
▪ RIGHT: Split mode, output on the right side
Explanation: HDMI signal on the O1A and O1B of the receiver is downsampled to YCbCr 4:2:0. For more
information see section.Output Conversion Modes
6.6.13. Setting the Output Conversion Mode of the Remote Device
INFO: This command is available for HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro model.
Output conversion mode on the O1A and O1B ports of the receiver can be also set by sending a command
to the trasmitter.
Command format: SET●/REMOTE/D1.Conversion=OFF|420|LEFT|RIGHT
Response format: pw●/REMOTE/D1.Conversion=OFF|420|LEFT|RIGHT
Example:
˃SET /REMOTE/D1.Conversion=LEFT
˂pw /REMOTE/D1.Conversion=LEFT
Legend: See previous legend.
Explanation: HDMI signal is splitted on the O1A (left) and O1B (right) ports of the receiver. For more infor-
mation see section.Output Conversion Modes
6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 50
6.7. Network Conguration
6.7.1. Querying the IP Address
Command format: GET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.IpAddress
Response format: pr●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.IpAddress=<IP_Address>
Example:
˃GET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.IpAddress
˂pr /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.IpAddress=192.168.0.101
6.7.2. Changing the IP Address (Static)
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticIpAddress=<IP_address>
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticIpAddress=<IP_address>
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticIpAddress=192.168.0.103
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticIpAddress=192.168.0.103
6.7.3. Querying the Subnet Mask
Command format: GET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask
Response format: pr●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask=<netmask>
Example:
˃GET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask
˂pr /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask=255.255.255.0
6.7.4. Changing the Subnet Mask (Static)
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask=<netmask>
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask=<netmask>
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask=255.255.255.0
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask=255.255.255.0
6.7.5. Querying the Gateway Address
Command format: GET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.GatewayAddress
Response format: pr●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.GatewayAddress=<gw_address>
Example:
˃GET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.GatewayAddress
˂pr /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.GatewayAddress=192.168.0.1
6.7.6. Changing the Gateway Address (Static)
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticGatewayAddress=<gw_address>
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticGatewayAddress=<gw_address>
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticGatewayAddress=192.168.0.5
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticGatewayAddress=192.168.0.5
6.7.7. Querying the DHCP State
Command format: GET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=true|false
Example:
˃GET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=true
6.7.8. Changing the DHCP State
Command format: SET●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=true|false
Response format: pw●/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=true|false
Example:
˃SET /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=false
˂pw /MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled=false
6.7.9. Enabling Ethernet Port
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/ETHERNET/<P n>.Enabled=true|false
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/ETHERNET/<P n>.Enabled=true|false
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/ETHERNET/P2.Enabled=false
˂pw /MEDIA/ETHERNET/P2.Enabled=false
Explanation: Disabled the P2 Ethernet port.

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 51
6.8. RS-232 Port Conguration
6.8.1. Querying the RS-232 Opearation Mode
Command format: GET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Rs232Mode
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Rs232Mode
Legend:
▪ 0: Pass-through
▪ 1: Control (local)
▪ 2: Command injection (local)
Example:
˃GET /MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode
6.8.2. Setting the RS-232 Opearation Mode
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Rs232Mode=0|1|2
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Rs232Mode=0|1|2
Legend: See the previous legend.
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode=1
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode=1
6.8.3. Setting the BAUD Rate
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Baudrate=0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Baudrate=0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7
Parameters:
.Baudrate 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
BAUD rate value 4800 7200 9600 14400 19200 38400 57600 115200
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.Baudrate=2
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.Baudrate=2
6.8.4. Setting the Databit
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.DataBits=8|9
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.DataBits=8|9
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.DataBits=8
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.DataBits=8
6.8.5. Setting the Stopbits
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.StopBits=0|1|2
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.StopBits=0|1|2
Parameters:
.StopBits 0 1 2
Stopbit value 1 1,5 2
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.StopBits=0
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.StopBits=0
6.8.6. Setting the Parity
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Parity=0|1|2
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.Parity=0|1|2
Parameters:
.Parity 0 1 2
Parity setting no parity odd even
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.Parity=0
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.Parity=0

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 52
6.8.7. Enabling Command Injection Mode
Command format: SET●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.CommandInjectionEnable=true|false
Response format: pw●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.CommandInjectionEnable=true|false
Example:
˃SET /MEDIA/UART/P1.CommandInjectionEnable=true
˂pw /MEDIA/UART/P1.CommandInjectionEnable=true
ATTENTION! The Command injection status is stored in another read-only property:
/MEDIA/UART/<P1>.CommandInjectionStatus.
6.9. Sending Message via the Communication Ports
6.9.1. Sending Message via an RS-232 Port
The RS-232 ports can be used for sending a command message to a device which can be controlled over
serial port. Both local RS-232 and extended link RS-232 ports can be used. The three different commands
allow to use different message formats.
Sending Message
The command is for sending a command messages in ASCII-format with an option for escaping special charaters.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.sendMessage(<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>:sendMessage
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendMessage(PWR0\x0d\x0a)
˂mO /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendMessage
Escaping in the Message
When commands need to be separated by <CR><LF> charaters to be recognized by the controlled device,
then they need to be escaped. You can use the following format for escaping:
<command 1><\x0d\x0a><command 2><\x0d\x0a>...<command n><\x0d\x0a>
See more details in section.Escaping
Sending Text Message
The command is for sending a text message in ASCII-format.
INFO: Escaping will not be processed using the sendText command.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.sendText(<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>:sendText
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendText(pwr_on)
˂mO /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendText
Sending Binary Message
The command is for sending a binary message in HEX format.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>.sendBinaryMessage(<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/UART/<P 1>:sendBinaryMessage
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendBinaryMessage(1100000061620000cdcc2c40)
˂mO /MEDIA/UART/P1:sendBinaryMessage
6.9.2. Sending Message via TCP Port
The device can be used for sending a message to a certain IP:port address. The three different commands
allow controlling the connected (third-party) devices.
Sending TCP Message
The command is for sending a command messages in ASCII-format with an option for escaping special charaters.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpMessage(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpMessage
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpMessage(192.168.0.20:5555=PWR0\x0d\x0a)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpMessage
Escaping in the Message
When commands need to be separated by <CR><LF> charaters to be recognized by the controlled device,
then they need to be escaped. You can use the following format for escaping:
<command 1><\x0d\x0a><command 2><\x0d\x0a>...<command n><\x0d\x0a>
See more details in section.Escaping

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 53
Sending Text Message
The command is for sending a text message in ASCII-format.
INFO: Escaping will not be processed using the tcpText command.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpText(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpText
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpText(192.168.0.20:5555=pwr_on)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpText
Sending Binary Message
The command is for sending a binary message in HEX format.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpBinary(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpBinary
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpBinary(192.168.0.20:5555=0100000061620000cdcc2c40)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpBinary
6.9.3. Sending Message via UDP Port
The device can be used for sending a message to a certain IP:port address. The three different commands
allow controlling the connected (third-party) devices.
Sending UDP Message
The command is for sending a command messages in ASCII-format with an option for escaping special charaters.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpMessage(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpMessage
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpMessage(192.168.0.20:5555=PWR0\x0d\x0a)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpMessage
Escaping in the Message
When commands need to be separated by <CR><LF> charaters to be recognized by the controlled device,
then they need to be escaped. You can use the following format for escaping:
<command 1><\x0d\x0a><command 2><\x0d\x0a>...<command n><\x0d\x0a>
See more details in section.Escaping
Sending Text Message
The command is for sending a text message in ASCII-format.
INFO: Escaping will not be processed using the udpText command.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpText(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpText
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpText(192.168.0.20:5555=pwr_on)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpText
Sending Binary Message
The command is for sending a binary message in HEX format.
Command format: CALL●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpBinary(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
Response format: mO●/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpBinary
Example:
˃CALL /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpBinary(192.168.0.20:5555=0100000061620000cdcc2c40)
˂mO /MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpBinary

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 54
6.10. EDID Management
6.10.1. Querying the Emulated EDIDs
Command format: GET●/EDID.EdidStatus
Response format: pr●/EDID.EdidStatus=<E_loc>:<E 1>;<E_loc>:<E
2>
Example:
˃GET /EDID.EdidStatus
˂pr /EDID.EdidStatus=D1:E1;D1:E2
Explanation:
Dynamic EDID was emulated for both input port.
6.10.2. Querying the Validity of a Dynamic EDID
Command format: GET●/EDID/D/D n.Validity
Response format: pr●/EDID/D/D n.Validity=true|false
Example:
˃GET /EDID/D/D1.Validity
˂pr EDID/D/D1.Validity=true
Explanation:
The ‘Validity’ property is true, valid EDID is stored in D1 memory place.
6.10.3. Querying the Preferred Resolution of an User EDID
Command format: GET●/EDID/U/U n.PreferredResolution
Response format: pr●/EDID/U/U n.PreferredResolution=<preferred_resolution>
Example:
˃GET /EDID/U/U1.PreferredResolution
˂pr /EDID/U/U1.PreferredResolution=3840x2160p60.00Hz
INFO: Use the "Manufacturer" property to query the manufacturer and the "MonitorName" property to
query the name of the monitor.
6.10.4. Emulating an EDID to an Input Port
Command format: CALL●/EDID:switch(<source>:<destination>)
Response format: mO●/EDID:switch
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:switch(F144:E2)
˂mO /EDID:switch
Legend:
▪ <source>: Source EDID memory place: Factory / User / Dynamic.
▪ <destination>: The emulated EDID memory of the desired input port.
6.10.5. Copying an EDID to User Memory
Command format: CALL●/EDID:copy(<D n>|<En>|<Fn>|<U
n>:<U
m>)
Response format: mO●/EDID:copy
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:copy(D1:U1)
˂mO /EDID:copy
Explanation:
The EDID of the last connected sink of D1 (Output 1) has been copied to U2.
6.10.6. Deleting an EDID from User Memory
Command format: CALL●/EDID:delete(<U n>)
Response format: mO●/EDID:delete
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:delete(U1)
˂mO /EDID:delete
6.10.7. Resetting the Emulated EDIDs
Command format: CALL●/EDID:reset(1)
Response format: mO●/EDID:reset
Example:
˃CALL /EDID:reset(1)
˂mO /EDID:reset
Explanation: Calling this method switches all emulated EDIDs to factory default one. See the table in the
Factory EDID List section.

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 55
6.11. LW3 Commands - Quick Summary
System Commands
Operation / Path
6.5.1 Querying the Product Name
.ProductName
6.5.2 Setting the Device Label
/MANAGEMENT/UID/DeviceLabel
6.5.3 Querying the Serial Number
.SerialNumber
6.5.4 Querying the Firmware Version
/SYS/MB.FirmwareVersion
6.5.5 Resetting the Extender
/SYS:reset()
6.5.6 Restoring the Factory Default Settings
/SYS:factoryDefaults()
6.5.7 Locking Front Panel
/MANAGEMENT/UI_ControlLock
6.5.8 Enabling Dark Mode
SET /MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeEnable
6.5.9 Setting the Dark Mode Delay
/MANAGEMENT/UI/DARKMODE.DarkModeDelay
6.5.10 Setting the Dark Mode on the Remote Device
/REMOTE/D1.DarkModeEnable
6.5.11 Setting the Rotary Direction of the Jog Dial Knob
/MANAGEMENT/UI.RotaryDirection
Video Port and Crosspoint Settings
Operation / Path
6.6.1 Querying the Crosspoint Setting
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationConnectionList
6.6.2 Switching Video Input
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:switch(<input>:<output)
6.6.3 Querying the Status of Source Ports
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.SourcePortStatus
6.6.4 Querying the Status of Destination Ports
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortStatus
6.6.5 Muting Input Port
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:muteSource(<input>)
6.6.6 Unmuting Input Port
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unmuteSource(<input>)
Operation / Path
6.6.7 Locking Input Port
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:lockSource(<input>)
6.6.8 Unlocking Input Port
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:unlockSource(<input>)
6.6.9 Querying the Video Autoselect Settings
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP.DestinationPortAutoselect
6.6.10 Changing the Autoselect Mode
/MEDIA/VIDEO/XP:setDestinationPortAutoselectoutput(<output>:<output_set>)
6.6.12 Setting the Output Conversion Mode
/MEDIA/VIDEO/<output>.Conversion
6.6.13 Setting the Output Conversion Mode of the Remote Device
/REMOTE/<output>.Conversion
Network Conguration
Operation / Path
6.7.1 Querying the IP Address
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.IpAddress
6.7.2 Changing the IP Address (Static)
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticIpAddress
6.7.3 Querying the Subnet Mask
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.NetworkMask
6.7.4 Changing the Subnet Mask (Static)
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask
6.7.5 Querying the Gateway Address
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.GatewayAddress
6.7.6 Changing the Gateway Address (Static)
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticGatewayAddress
6.7.7 Querying the DHCP State
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled
6.7.8 Changing the DHCP State
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.DhcpEnabled
6.7.9 Enabling Ethernet Port
/MEDIA/ETHERNET/<port_no>.Enabled

6. LW3 Programmers’ Reference HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 56
RS-232 Port Conguration
Operation / Path
6.8.1 Querying the RS-232 Opearation Mode
/MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode
6.8.2 Setting the RS-232 Opearation Mode
/MEDIA/UART/P1.Rs232Mode
6.8.3 Setting the BAUD Rate
/MEDIA/UART/P1.Baudrate
6.8.4 Setting the Databit
/MANAGEMENT/NETWORK.StaticNetworkMask
6.8.5 Setting the Stopbits
/MEDIA/UART/P1.StopBits
6.8.6 Setting the Parity
/MEDIA/UART/P1.Parity
6.8.7 Enabling Command Injection Mode
/MEDIA/UART/P1.CommandInjectionEnable
Sending Message via the Communication Ports
Operation / Path
6.9.1
Sending Message via an RS-232 Port
/MEDIA/UART/P1:sendMessage(<message>)
/MEDIA/UART/P1:sendText(<text>)
/MEDIA/UART/P1:sendBinaryMessage(<binarymessage>)
6.9.2
Sending Message via TCP Port
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpMessage(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpText(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:tcpBinary(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
6.9.3
Sending Message via UDP Port
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpMessage(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpText(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
/MEDIA/ETHERNET:udpBinary(<IP_address>:<port_no>=<message>)
EDID Management
Operation / Path
6.10.1 Querying the Emulated EDIDs
/EDID.EdidStatus
6.10.2 Querying the Validity of a Dynamic EDID
/EDID/D/D1.Validity
6.10.3 Querying the Preferred Resolution of an User EDID
/EDID/U/U1.PreferredResolution
6.10.4 Emulating an EDID to an Input Port
/EDID:switch(<source>:<destination>)
6.10.5 Copying an EDID to User Memory
/EDID:copy(<source>:<destination>)
6.10.6 Deleting an EDID from User Memory
/EDID:delete(<user_edid_memory>)
6.10.7 Resetting the Emulated EDIDs
/EDID:reset(1)

7. Firmware Upgrade HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 57
ATTENTION!
operation mode is suspended as the extender is switched to
bootload mode. Signal processing is not performed. Do not interrupt
restart the process.
ATTENTION!
please see the section before
the upgrade.
7.1. About the Firmware Package (LFP File)
INFO:
and the receiver.
▪ The package contains all the necessary components, binary,
▪
the LDU.
7.2. Short Instructions
Step 1.
application.
Step 2. Install the LDU application.
Step 3. Establish the connection between the computer and the
device(s) over the Ethernet interface.
Step 4. Start the LDU and follow the instructions shown on the screen.
7.3. Install and Upgrade
Installation for Windows OS
Run the installer. If the User Account Control drops a pop-up message
click Yes. During the installation you will be prompted to select the
type of the installation
7
Firmware Upgrade
This chapter is meant to help customers perform rmware upgrades on our
products by giving a few tips on how to start and by explaining the features of
the Lightware Device Updater (LDU) software. To get the latest software and
rmware pack can be downloaded from www.lightware.com.
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Normal install Snapshot install
The installer can update only this instance Cannot be updated
Only one updateable instance can exist
for all users
More than one different version
can be installed for all users
Comparison of install types
ATTENTION! Using the Normal install as the default value is highly
recommended.
Installation for Mac OS X
has the same look and functionality. This type of the installer is
updateable version with the same attributes.
over the Applications icon to copy the program into the Applications
folder. If you want to copy the LDU into another location just drag the
icon over the desired folder.
LDU Upgrade
Step 1. Run the application. In the welcome screen click on the
button in the top right corner; the About window will appear.
Click on the button. The program checks the available Check now
updates on Lightware website and shows its version.
?
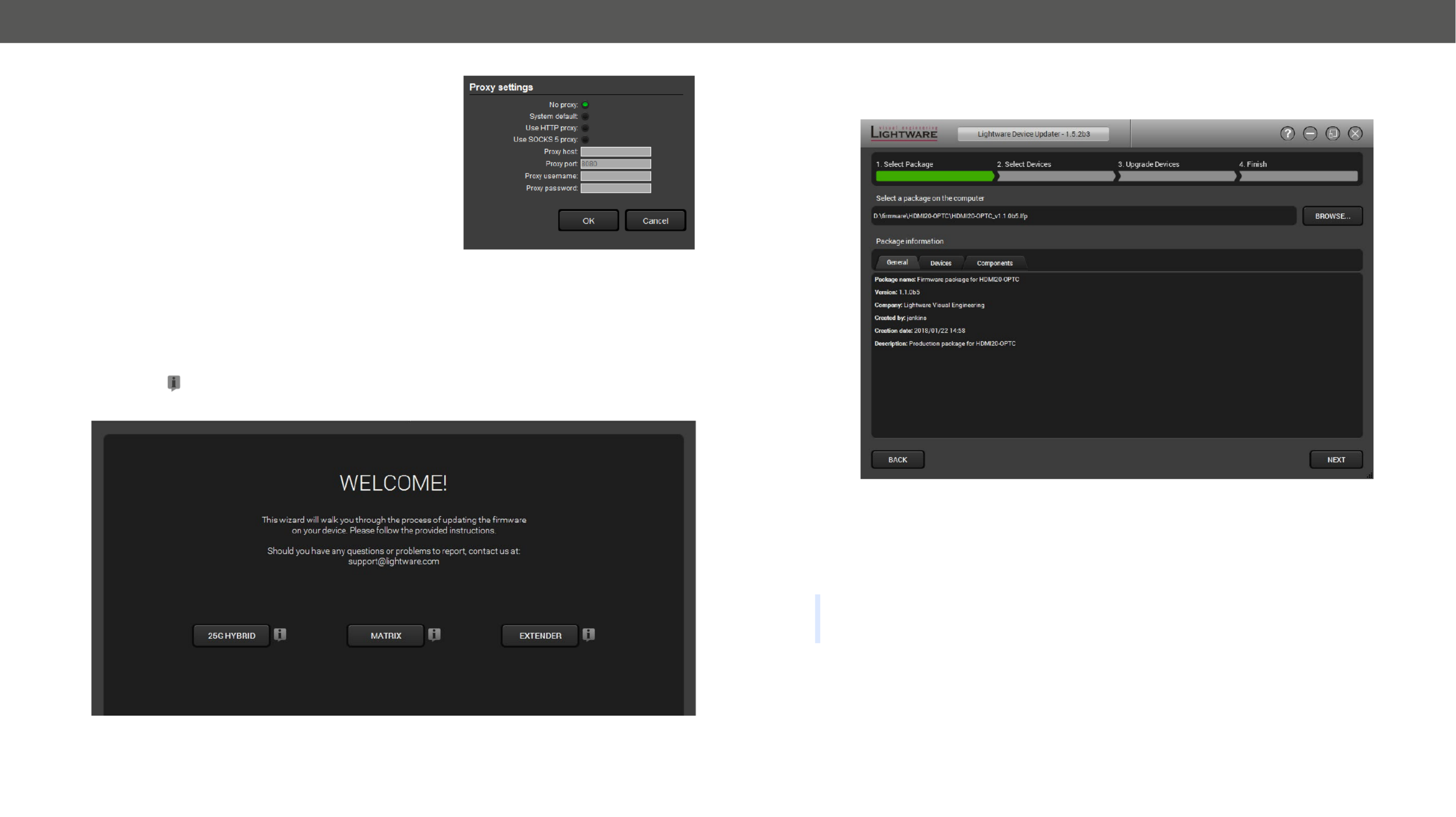
7. Firmware Upgrade HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 58
Step 2. OptionsSet the desired update settings in the section.
▪ If you do not want to check for the updates automatically,
uncheck the , which contains the green tick.circle
▪ If you want to postpone the update, a reminder can be set
with different delays from the .drop down list
▪ If the proxy settings traverse the update process, set the
proper values then click the button.OK
Step 3. UpdatePress the button to download the new version; the
installer will start.
7.4. Detailed Instructions
7.4.1. Establish the Connection
Make sure that the computer and the device are connected via an Ethernet cable and the connection is
established between them.
7.4.2. Start the LDU and Follow the Instructions
After launching LDU the welcome screen will appear
Pressing the button a list will appear showing the supported devices:
Click on the button on the main screen.Extender
Step 1. Select the package.
Click on the Browse button and select the “.lfp” le that will be used for the upgrade.
Package information is displayed:
▪ General version info, creation date, short description,
▪ Devices which are compatible with the rmware,
▪ Components in the package with release notes.
Click on the button and follow the instructions.Next
TIPS AND TRICKS: Files with “.lfp” extension are associated to LDU during installation. If you double click
on the “.lfp” le, the application is launched, the package is loaded automatically and the above screen is
shown.

7. Firmware Upgrade HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 59
Step 2. Select device.
The following step is to select the desired device(s). The available and supported devices are searched and
listed automatically. If the desired device is not listed, update the list by clicking the button. Select Refresh
the desired devices: highlight them with a yellow cursor, OK then click .
A tick mark can be seen in the column if the device was added by the user previously.Added
Firmware Components
The rmware components of the selected devices are listed on the following screen: installed and update
versions. (Update version will be uploaded to the device.)
Add a device by clicking on the button. The previous screen will be shown; select the desired Add device
device(s) and click on .OK
Remove a device by selecting it (highlight with yellow) and click on button, or click on Remove device Remove
all button to empty the list.
Enabling Factory reset will perform factory default values for all settings in the device. Three different status
can exist:
▪ Enabled by user: all settings will set to factory default values.
▪ Disabled by user: your settings will be saved and restored after upgrading.
▪ Enabled by default and not changeable by user: rmware upgrade must perform a factory reset to apply all
changes coming with the new rmware version.
Click on the button to continue.Next

7. Firmware Upgrade HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 60
Step 3. Upgrade the device.
Click on the button to continue.Start
A warning window will pop up before starting upgrading the device:
▪ Do not unplug the power cable and the LAN cable while the upgrade is in progress. Click to continue.OK
After you conrmed the warnings and clicked on the Start button, the upgrade process starts immediately.
Details button opens a new window where the process is logged – see below.

7. Firmware Upgrade HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 61
Step 4. Finish.
If the upload of the rmware package is nished, LDU gives a message in a pop up-window:
After that, the extender starts the self-upgrade procedure.
ATTENTION! Do not disconnect the power supply or the Ethernet cable! It is an automatic action and no
user interruption is needed during the operation. The red LEDs show the status of the process. When none
of the LEDs light red, the upgrade is nished.
On the summary page logs can be opened by button or exported with button. Click Open Logs Export Logs Exit
to close or to begin the upgrade process again.Repeat
ATTENTION! However the device is rebooted after the rmware upgrade, switching it off and on again is
recommended.
Upload
Firmware
package
Self upgrade
process
LDU LW Device
7.5. Keeping the Conguration Settings
User can keep all conguration settings and restore to the device after rmware upgrading or can choose to
perform a factory reset – it means all settings will be erased in the device. In case of factory reset you can
save the settings of the device and restore it later. For the detailed information about saved data refer to the
Content of Backup File section.
The following ow chart demonstrates how this function works in the background.
Flow chart of rmware upgrade
The details about the procedure:
when rmware upgrade starts, the
rst step is making a backup of the
settings of the device. The rmware
package checks the backup data and
if it is needed, a conversion is applied
to avoid incompatibility problems
between the rmware versions. If you
do not want to keep conguration
settings, you can set the Factory reset
option enabled.
The instruction in the rmware
package of the device will inform
you about this function availability,
reading it is highly recommended in
every case.
Select devices page in the rmware package
ATTENTION! In specic cases restoring cannot be applied fully and certain settings are not copied back
to the device. If a warning message appears, user can get back the original data from the backup. Logs
of the upgrade procedure contain all backup data, it can be exported at the end of the upgrade procedure.
Details about the procedure of log exporting can be found in the section. In case of Detailed Instructions
any question, please contac .t support@lightware.com
ATTENTION! In certain cases, the new rmware version requires setting all parameters to set factory
defaults. In this case, the “Factory reset” option is enabled by default and not changeable by the user, see
details in the section.Detailed Instructions
ATTENTION! The feature is only supported by LDU version 1.3.0 and above.
Backup Conversion/Restore
Start Factory reset EndUpgrading
8. Troubleshooting HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 62
8
Troubleshooting
Usually, if the system seems not to transport the signal as expected, the best strategy for troubleshooting is to
check signal integrity through the whole signal chain starting from source side and moving forward to receiver end.
Link to connections/cabling section.
Link to front panel operation section.
Link to LDC software section.
LW3
Link to LW3 protocol commands section
At rst, check front panel LEDs and take the necessary steps according to their states. For more information
about status, LEDs refer to the and sections.Front View Rear View
Symptom Root cause Action Refer to
Video signal
No picture on the
video output
Device(s) not powered
properly.
Check the extenders and the other devices
if they are properly powered; try to unplug
and reconnect them.
3.3
Cable connection
problem.
Due to the high data rates cables must t
very well, check all the connectors. If your
source or display has more connectors
then make sure that the proper port is
selected.
3.3
Cable quality problem.
Due to the high data rates, high quality
cables must be used. It is recommended
to use OM3 or OM4 ber cables.
10.4
Endface surface of the
ber optical cable
became contaminated.
Use special ber optical cable cleaning
equipment to clean it carefully.
Display is not capable of
receiving the sent video
format.
Try emulating your display device’s EDID
to the source.
4.3.3
5.5
LW3
6.10.4
Source power and
conguration problems.
Check whether your source is powered on
and congured properly. The HDMI output
can be turned off on most DVD players. If
the source is a computer, then verify that
the HDMI output is selected and active.
Try restarting your computer; if you get
a picture during the booting process, you
have to review the driver settings.
HDMI output
signal contains no
audio
Video signal type was
set to DVI.
Check the signal type properties of the
output port and set to HDMI or Auto.
5.4.2
5.4.4
DVI EDID is emulated. Check the EDID and select and HDMI EDID
to emulate.
4.3.3
5.5
LW3
6.10.1

8. Troubleshooting HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 63
Symptom Root cause Action Refer to
RS-232 signal
Connected serial
device cannot be
controlled
Cable connection
problem
Check whether your serial cable is
properly connected and check the wiring
of the plugs.
3.3
RS-232 mode is not right Check the RS-232 mode settings (pass,
control and command injection)
4.3.1
5.6.1
LW3
6.8.1
Network
No LAN
connection can be
established
Incorrect IP address is
set (x IP)
Use dynamic IP address by enabling
DHCP option.
4.3.1
5.8.2
LW3
6.7.8
Restore the factory default settings (with
x IP).
4.3.1
5.6.1
LW3
6.5.6
IP address conict Check the IP address of the other
devices, too. 5.2
Miscellaneous
No LEDs are light Dark mode is enabled Disable the dark mode
4.3.1
4.3.5
5.8.3
LW3
6.6.12
Select/function
button not toggles
the inputs/
conversion modes
Front panel buttons are
locked Unlock the buttons.
5.8.3
LW3
6.5.7
How to Speed up the Troubleshooting Process?
Lightware’s technical support team
is always working hard to provide the
fastest support possible. Our team’s
response time is one of the best in the
industry and in the toughest of cases we
can directly consult with the hardware
or software engineer who designed the
product to get the information from the
most reliable source.
However, the troubleshooting process can be even faster… with your help.
There are certain pieces of information that push us in the right direction to nding the root cause of the
problem. If we receive most of this information in the rst e-mail or it is gathered at the time when you call
us, then there is a pretty high chance that we will be able to respond with the nal solution right away.
This information is the following:
▪ Schematic (a pdf version is preferred, but a hand drawing is sufcient).
▪ Serial number(s) of the device(s) (it is either printed somewhere on the box or you can query it in the
Device Controller software or on the built-in website).
▪ Firmware versions of the devices (please note that there may be multiple CPUs or controllers in the
device and we need to know all of their rmware versions, a screenshot is the best option).
▪ Cable lengths and types (in our experience, it’s usually the cable).
▪ Patch panels, gender changers or anything else in the signal path that can affect the transmission.
▪ Signal type (resolution, refresh rate, color space, deep color).
▪ Emulated EDID(s) (please save them as le and send them to us).
▪ Actions to take in order to re-create the problem (if we cannot reproduce the problem, it is hard for us
to nd the cause).
▪ Photo or video about the problem (‘image noise’ can mean many different things, it’s better if we see
it too).
▪ Error logs and backup les from the Lightware Device Controller software.
The more of the above information you can give us the better. Please send these information to the Lightware
Support Team to speed up the troubleshooting process.
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter

9. Technologies HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 65
9.2. HDCP Management
Lightware Visual Engineering is a legal HDCP adopter. Several
functions have been developed which helps to solve HDCP related
problems. Complex AV systems often have both HDCP and non-HDCP
components. The extender allows transmitting HDCP encrypted and
unencrypted signals. The devices will be still HDCP compliant as they
will never output an encrypted signal to a non-HDCP compliant display
device. If an encrypted signal is switched to a non-compliant output, a
red screen alert or muted screen will appear.
9.2.1. Protected and Unprotected Content
Many video sources send HDCP protected signal if they detect that
the sink is HDCP capable – even if the content is not copyrighted. This
can cause trouble if an HDCP capable device is connected between
the source and the display. In this case, the content cannot be viewed
on non-HDCP capable displays and interfaces like event controllers.
Rental and staging technicians often complain about certain laptops,
which are always sending HDCP encrypted signals if the receiver
device (display, extender router, etc.) reports HDCP compliancy.
However, HDCP encryption is not required all the time e.g. computer
desktop image, certain laptops still do that.
To avoid unnecessary HDCP encryption, Lightware introduced the
HDCP enabling/disabling function: the HDCP capability can be
disabled in the Lightware device. If HDCP is disabled, the connected
source will detect that the sink is not HDCP capable, and turn off
authentication.
9.2.2. Disable Unnecessary Encryption
HDCP Compliant Sink
Protected
content
HDCP-complian
sink
Encrypted
signal
HDMI cable HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
Encrypted
signal
HDMI cableOptical
cable
Transmitter Receiver
All the devices are HDCP-compliant, no manual setting is required, both
protected and unprotected contents are transmitted and displayed on
the sink.
Not HDCP-compliant Sink 1.
Unprotected
content
Non-HDCP
compliant sink
Non-Encrypted
signal
HDMI cable HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter
Non-Encrypted
signal
HDMI cableOptical
cable
Transmitter Receiver
Non-HDCP compliant sink is connected to the extender. Some
sources (e.g. computers) always send HDCP encrypted signals if the
receiver device reports HDCP compliancy, however, HDCP encryption
is not required all the time (e.g. computer desktop image). If HDCP is
enabled in the extender, the image will not be displayed on the sink.
Setting the HDCP parameter to Auto on the output port and disable
HDCP on the input port, the transmitted signal will not be encrypted
if the content is not protected. Thus, non-HDCP compliant sinks will
display non-encrypted signal.
Not HDCP-compliant Sink 2.
Encrypted
signal
HDMI cable HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Receiver
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
SIGNAL PRESENT
OUTPUT CONVERSION
CONTROL
FUNCTION
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
MAIN MENU
> System Settings
Ports
EDID
Health
Remote
POWER / LIVE
FIBER LINK
HDCP
INPUT 1
INPUT 2
CONTROL
SELECT
USB
HDMI20
OPTC
220-PRO
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
HDMI 2.0 Multimode Fiber Transmitter HDMI cableOptical
cable
Transmitter Receiver Non-HDCP
compliant sink
Protected
content
The layout is the same as in the previous case: non-HDCP compliant
display device is connected to the extender but the source would send
protected content with encryption. If HDCP is enabled on the input
port of the extender, the source will send encrypted signal. The sink
is not HDCP compliant, thus, it will not display the video signal (but
blank/red/muted/etc. screen). If HDCP is disabled on the input port
of the extender, the source will not send the signal. The solution is to
replace the display device to an HDCP-capable one.

9. Technologies HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 66
9.3. Pixel Accurate Reclocking
Signal reclocking is an essential important procedure in digital signal
transmission. After passing the reclocking circuit, the signal becomes
stable, jitter-free, and can be transmitted over more equipment like
processors, or event controllers. Without reclocking, sparkles, noise,
and jaggies appear on the image.
Lightware’s sophisticated Pixel Accurate Reclocking technology
xes more problems than general TMDS reclocking. It removes not
only intra-pair skew but inter-pair skew as well. The Pixel Accurate
Reclocking circuit eliminates the following errors:
Intra-pair skew
Skew between the + and - wires within a differential wire pair (e.g.
Data2- and Data2+). It’s caused by different wire lengths or slightly
different wire construction (impedance mismatch) in DVI cable. It
results in jitter.
Intra-pair skew
+
-
Inter-pair skew
Skew between two differential wire pairs in a cable. It is caused by
different wire pair lengths or different number of twists in the DVI
cable. Too much inter-pair skew results color shift in the picture or
sync loss.
+
-
Inter-pair skew
+
-
Jitter
Signal instability in the time domain. The time difference between two
signal transitions should be a xed value, but noise and other effects
cause variations.
Jitter
+
-
Noise
Electromagnetic interference between other electronic devices such
as mobile phones, motors, etc. and the DVI cable are coupled onto the
signal. Too much noise results in increased jitter.
Noise
+
-
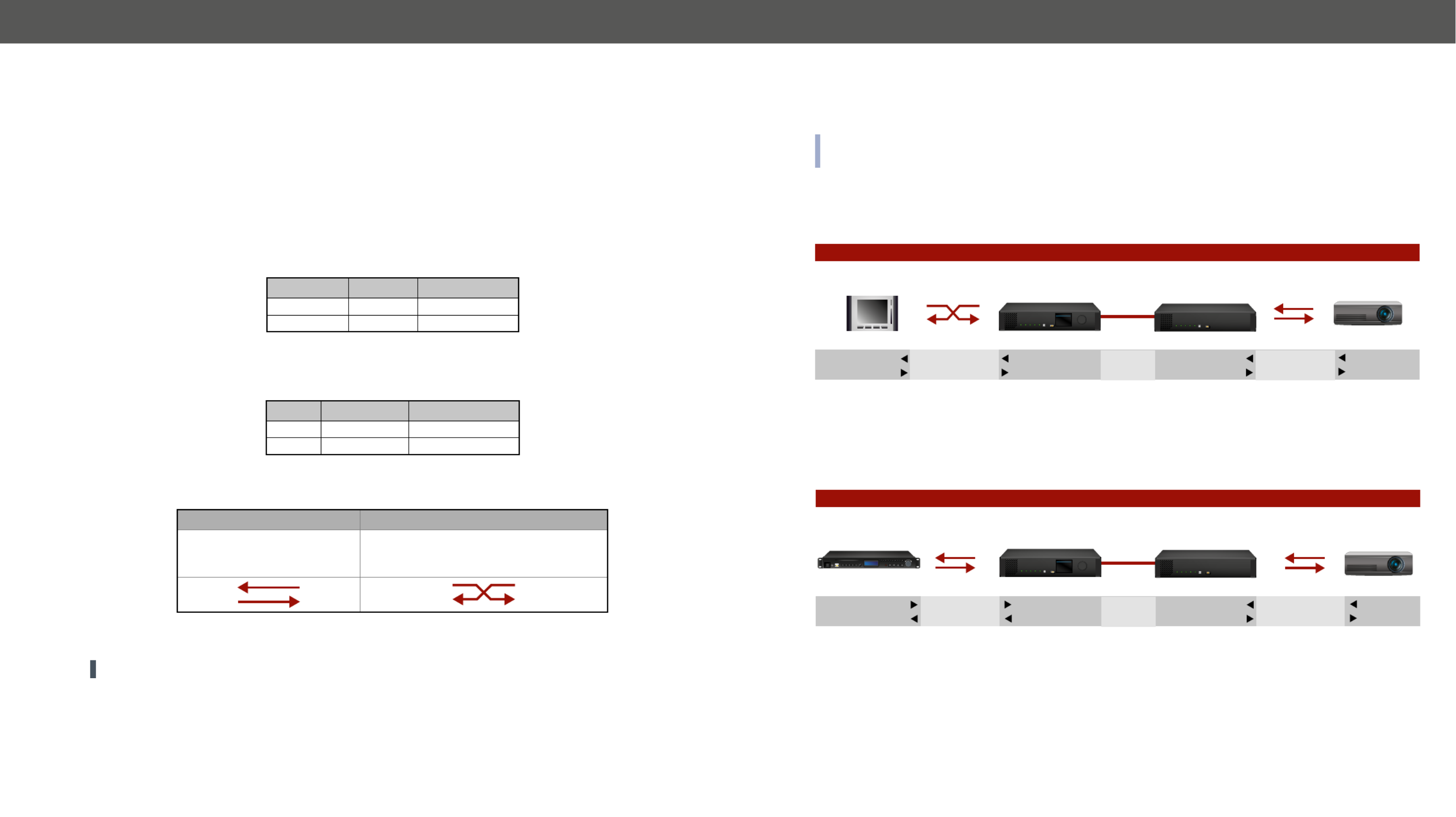
9. Technologies HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 67
9.4. Serial Management
9.4.1. General Information
There are two types of devices in general serial communication:
▪ Data Terminal Equipment: Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) is an end instrument that converts user
information into signals or reconverts received signals. Typical DTE devices: computers, LCD touch
panels and control systems.
▪ Data Circuit-terminating Equipment: Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) is a device that sits
between the DTE and a data transmission circuit. It is also called data communication equipment and
data carrier equipment. Typical DCE devices: projectors, industrial monitors and ampliers.
Among others the pin assignment is different between DTE and DCE.
DTE DCE
Pin 2: RD TD
Pin 3: TD RD
RD: Received Data (digital input)
TD: Transmitted Data (digital output)
Different type of serial cables must be used between different serial devices.
DTE DCE
DTE Null-modem Straight
DCE Straight Null-modem*
* In general contact DCE with DCE by tail-circuit serial cable.
9.4.2. Types of Serial Cables
Straight Serial Cable Null-modem Serial Cable
Straight pin-outs both ends. Straight pin-out at the one end and cross
pin-out at the other end (interchange lines
of TX and RX).
Serial cables between devices may have male or female plugs and their type may be straight or null-modem
in usual.
ATTENTION! The cable type does not depend on the plug type.
9.4.3. RS-232 Signal Transmission over Lightware Extender Devices
The following examples describe the detailed integration of Lightware devices between different RS-232 pin
assignment units.
INFO: Both HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro and HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro are DTE units (according to their pinouts)
with male plugs.
Extending RS-232 between DTE and DCE third-party devices
Connect null-modem serial cable between controller system (DTE) and the transmitter (DTE) and straight
serial cable between receiver (DTE) and projector (DCE).
RS-232 connection example between a controller system and a projector
Extending RS-232 between DCE and DCE third-party devices
Connect straight serial cable between controller system (DTE) and the transmitter (DCE) and null-modem
serial cable between receiver (DTE) and computer (DTE).
RS-232 connection example between a media player and a projector
TransmitterController system Projector
Female - Female Female - Male
Transmission
interface
Straight serial
cable
Null-modem
serial cable DTE
Pin 2: RD
Pin 3: TD
Receiver
DTE
Pin 2: RD
Pin 3: TD
Pin 2: RD
Pin 3: TD
DTE DCE
Pin 2: TD
Pin 3: RD
Transmitter
Media Player Projector
Male - Female Female - Male
Transmission
interface
DTE
Pin 2: TD
Pin 3: RD
Receiver
DTE
Pin 2: RD
Pin 3: TD
Pin 2: RD
Pin 3: TD
DCE DCE
Pin 2: TD
Pin 3: RD
Straight serial
cable
Straight serial
cable

10. Appendix HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 68
10
Appendix
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
Ý
10.1. Specication
General
Compliance CE .........................................................................................
....................... EN 55035:2017, EN 55032:2015
RoHS compliance...............................................................................Yes
Safety EN 60065 Class I ...........................................................................
Cooling...................................................................................Cooling fan
Operating temperature ...............................
Storage temperature .................................
Operating humidity 10% to 80%, non-condensing ..................................
HDCP compliance ..............................................................................Yes
.......................................................................................3 years
Power
.................................................
...................................................
.................................................
......................................................
Enclosure
Rack mountable .................................................................................Yes
Material 1 mm steel ..................................................................................
Dimensions in mm (with device ears) ...........
..................................................................
Optical Port
Optical connector Neutrik opticalCON DUO LC .......................................
Optical break-out connector ................................................................LC
Fiber ..................
Laser forward wavelengths 5ch.: 778; 801; 824; 850; 911 nm ...............
Laser return wavelength .............................................................. 980nm
Transmission distance ..................
Video Ports
Port connector type.. 19-pole HDMI type A receptacle ..........................
Supported video formats .........................
Max. resolution 4096x2160@60Hz ........................................................
Color depth Deep color support up to 36 bits, ........................................
Color space .......................................................
..............................................................18 Gbps
..............................................................18 Gbps
.......................................................................9 Gbps
3D support ..........................................................................................Yes
Audio formats..................... all formats in line with HDMI 2.0 standard
EDID emulation Yes, Advanced EDID management ...............................
Reclocking.....................................................Pixel Accurate Reclocking
Control Ports
LAN
LAN connector Neutrik etherCON ...........................................................
Data rate ......................................................................................
RS-232 Control
Serial port connector D-SUB connector ..................................................
Available Baud rates between 4800 and 115200 ...................................
USB Control
USB connector USB mini B type ..............................................................
USB 2.0 compliance...........................................................................Yes

10. Appendix HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 69
10.2. Content of Backup File
Transmitter Receiver
HDMI Input (I1, I2)
Port name
Mute/ unmute input ports
Lock/ unlock input ports
Crosspoint settings
Optical Output (O1) Optical Input (I1)
Port name Port name
Mute/ unmute output port Mute/ unmute output port
Lock/ unlock output port Lock/ unlock output port
Autoselect settings
Signal type Signal type
HDMI Output (O2) HDMI Output (O1,O2,O3)
Port name Port name
Mute/ unmute output port Mute/ unmute output port
Lock/ unlock output port Lock/ unlock output port
Autoselect settings
Signal type Signal type
+5V Enable +5V Enable
RS-232 RS-232
Port name Port name
RS-232 mode RS-232 mode
Baud rate/ Data bits/ Stop bits/
Parity
Baud rate/ Data bits/ Stop bits/
Parity
Command injection enable/ Port Command injection enable/ Port
Control protocol Control protocol
Ethernet Ethernet
Port name (P1, P2, P3, P4) Port name (P1, P2, P3, P4)
Enable (P1, P2) Enable (P1, P2)
EDID Settings EDID Settings
User EDID U1-14 User EDID U1-13
Emulated EDIDs Emulated EDIDs
Event Manager Event Manager
Events 1-20 Events 1-20
Front Panel Control Front Panel Control
Display brightness
Rotary direction
Control lock
Dark mode enable Dark mode enable
Transmitter Receiver
Dark mode delay Dark mode delay
Device label Device label
Network Network
DHCP enable DHCP enable
Static IP address Static IP address
Static network mask Static network mask
Static gateway address Static gateway address
Remote device (Receiver)
Conversion mode
O1 +5V Enable
O2 +5V Enable
O3 +5V Enable
10.3. Factory Default Settings
Factory Default Settings of the HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
Transmitter
Video settings: HDMI Input
Port number I1, I2
Port name HDMIIN1, HDMIIN2
Mute/ unmute input ports Unmuted
Lock/ unlock input ports Unlocked
Crosspoint settings I1:O1; I1:O2
Video settings: Optical Output
Port name OPTOUT
Port number O1
Mute/ unmute output port Unmuted
Lock/ unlock output port Unlocked
Autoselect settings Disabled
Signal type Auto
Video settings: HDMI Output
Port name HDMIOUT
Port number O2
Mute/ unmute output port Unmuted
Lock/ unlock output port Unlocked
Autoselect settings Disabled
Signal type Auto
+5V Enable Always on
Transmitter
Front panel settings
Display brightness 10
Rotary direction CW
Control lock Unlock
Dark mode enable, dark mode
delay Disable
General
Device label HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-PRO
Network
DHCP enable Disabled
Static IP address 192.168.0.101
Static network mask 255.255.255.0
Static gateway address 192.168.0.1
Remote device (Receiver)
Conversion mode No conversion
O1 +5V Enable (Output 1/A) Always on
O2 +5V Enable (Output 1/B) Always on
O3 +5V Enable (Output 2) Always on

10. Appendix HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 70
Factory Default Settings of the HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
Receiver
Video settings: Optical Input
Port name OPTIN
Port number I1
Mute/ unmute input ports Unmute
Lock/ unlock input ports Unlock
Video settings: HDMI Output
Port name HDMIOUT1A, HDMIOUT1B, HDMIOUT2
Port number O1, O2, O3
Mute/ unmute output port Unmuted
Lock/ unlock output port Unlocked
Signal type Auto
+5V Enable Always on
Conversion mode* No conversion
Front panel
Control lock Unlock
Dark mode enable, dark
mode delay Disable
General
Device label HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-PRO
Network
DHCP enable Disabled
Static IP address 192.168.0.102
Static network mask 255.255.255.0
Static gateway address 192.168.0.1
* This setting is only available at HDMIOUT1A (O1) port.
Factory Default Settings of the HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro and
HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro
Transmitter Receiver
RS-232
Port name Local
RS-232 mode Pass-through
Baud rate 57600
Data bits 8
Stop bits N
Parity 1
Command injection enable Disabled
Port 8001
Control protocol LW2
Ethernet
Port name (P1, P2, P3, P4) Ethernet, Ethernet, OPT, CPU
Enable (P1, P2) Enable
EDID Settings
Emulated EDIDs D1* for all inputs
Front panel
Display brightness 10
Rotary direction CW
Control lock Unlock
Dark mode enable, dark mode
delay Disable
Remote device (Receiver)
Conversion mode No conversion
O1 +5V Enable (Output 1/A) Always on
O2 +5V Enable (Output 1/B) Always on
O3 +5V Enable (Output 2) Always on
*The default emulated EDID is D1 both the transmitter and the receiver.
The EDID, which is from the attached monitor of HDMIOUT1A (O1)
port of the receiver, is copied to all the input ports.
10.4. Maximum Extension Distances
The below table shows the transmission distances via optical cable
between the HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-Pro HDMI20-OPTC-RX220-Pro
depending on the cable quality and pixel clock frequency.
Resolution, Pixel clock rate Cable lengths
OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4
1280x720p60 Hz 800m 1000m 2500m 2500m
1920x1080p60 Hz 500m 1000m 2500m 2500m
3840x2160p30 Hz (4k30 4:4:4) 200m 600m 1500m 1500m
3840x2160p60 Hz (4k60 4:2:0)
3840x2160p60 Hz (4k60 4:4:4) Not
supported 300m 700m 700m
4096x2160p60 Hz (DCI 4K60)

10. Appendix HDMI20-OPTC series – User's Manual 71
10.5. Factory EDID List
Mem. Resolution Type
F1 640 x 480 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F2 848 x 480 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F3 800 x 600 @ 60.32 Hz DVI
F4 1024 x 768 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F5 1280 x 768 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F6 1280 x 768 @ 59.94 Hz DVI
F7 1360 x 768 @ 75.00 Hz DVI
F8 1360 x 768 @ 60.02 Hz DVI
F9 1280 x 1024 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F10 1280 x 1024 @ 60.02 Hz DVI
F11 1280 x 1024 @ 75.02 Hz DVI
F12 1400 x 1050 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F13 1400 x 1050 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F14 1400 x 1050 @ 75.00 Hz DVI
F15 1680 x 1050 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F16 1920 x 1080 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F17 1920 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F18 2048 x 1080 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F19 2048 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F20 1600 x 1200 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F21 1600 x 1200 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F22 1920 x 1200 @ 50.00 Hz DVI
F23 1920 x 1200 @ 59.56 Hz DVI
F24 2048 x 1200 @ 59.96 Hz DVI
F25-F28 Reserved
F29 Universal DVI EDID
F30 1440 x 480i @ 60.05 Hz HDMI
F31 1440 x 576i @ 50.08 Hz HDMI
F32 640 x 480 @ 59.95 Hz HDMI
F33 720 x 480 @ 59.94 Hz HDMI
F34 720 x 576 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F35 1280 x 720 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F36 1280 x 720 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F37 1920 x 1080i @ 50.04 Hz HDMI
Mem. Resolution Type
F38 1920 x 1080i @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F39 1920 x 1080i @ 60.05 Hz HDMI
F40 1920 x 1080i @ 60.05 Hz HDMI
F41 1920 x 1080 @ 24.00 Hz HDMI
F42 1920 x 1080 @ 25.00 Hz HDMI
F43 1920 x 1080 @ 30.00 Hz HDMI
F44 1920 x 1080 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F45 1920 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F46 1920 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F47 Universal HDMI EDID; PCM audio
F48 Universal HDMI EDID; all audio
F49 Universal HDMI EDID; all audio, deep color
F50-F89 Reserved
F90 1920 x 2160 @ 59.99 Hz DVI
F91 1024 x 2400 @ 60.01 Hz DVI
F92-F93 Reserved
F94 2048 x 1536 @ 60.00 Hz DVI
F95 Reserved
F96 2560 x 1600 @59.86 Hz DVI
F97 3840 x 2400 @24.00 Hz DVI
F98 1280 x 720 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F99 1920 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F100 1024 x 768 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F101 1280 x 1024 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F102 1280 x 1024 @ 60.02 Hz HDMI
F103 1280 x 1024 @ 75.02 Hz HDMI
F104 1600 x 1200 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI
F105 1600 x 1200 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F106 1920 x 1200 @ 59.56 Hz HDMI
F107 2560 x 1440 @ 59.95 Hz HDMI
F108 2560 x 1600 @ 59.86 Hz HDMI
F109 3840 x 2400 @ 24.00 Hz HDMI
F110 3840 x 2160 @ 24.00 Hz HDMI
F111 3840 x 2160 @ 25.00 Hz HDMI
F112 3840 x 2160 @ 30.00 Hz HDMI
Mem. Resolution Type
F113-F117 Reserved
F118 Universal HDMI EDID; 4K, PCM audio
F119 Universal HDMI EDID; 4K, all audio
F120 3840 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F121 1440 x 1080 @ 59.91 Hz HDMI
F122 2560 x 2048 @ 59.98 Hz HDMI
F123 1280 x 800 @ 59.91 Hz HDMI
F124 1440 x 900 @ 59.90 Hz HDMI
F125 1368 x 768 @ 59.85 Hz HDMI
F126 1600 x 900 @ 59.98 Hz HDMI
F127 2048 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F128 2560 x 1080 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F129 3440 x 1440 @ 24.99 Hz HDMI
F130 3440 x 1440 @ 29.99 Hz HDMI
F131 4096 x 2160 @ 25.00 Hz HDMI
F132 4096 x 2160 @ 30.00 Hz HDMI
F133 4096 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI
F134 3440 x 1440 @ 23.99 Hz HDMI
F135 4096 x 2160 @ 24.00 Hz HDMI
F136 3840 x 2400 @ 29.99 Hz HDMI
F137 3840 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F138 3840 x 2160 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F139 Universal HDMI 2.0 EDID; UHD, PCM audio
F140 Universal HDMI 2.0 EDID; UHD, all audio
F141 4096 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F142 4096 x 2160 @ 50.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F143 Universal HDMI EDID; 4K, PCM audio
F144 Universal HDMI EDID; 4K, all audio
F145 Reserved
F146 3840 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F147 3840 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
F148 3840 x 2160 @ 60.00 Hz HDMI 2.0
Specyfikacje produktu
| Marka: | Lightware |
| Kategoria: | przedłużacz AV |
| Model: | HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-FOX |
| Kolor produktu: | Czarny |
| Częstotliwość wejściowa AC: | 50 - 60 Hz |
| Napięcie wejściowe AC: | 100 - 240 V |
| Wysokość produktu: | 42.9 mm |
| Szerokość produktu: | 221 mm |
| Głębokość produktu: | 222.25 mm |
| Certyfikat środowiskowy (zrównoważonego rozwoju): | RoHS |
| Technologia łączności: | Przewodowa |
| Certyfikaty: | CE |
| Ilość portów USB: | 1 |
| Obsługiwany typ USB: | Mini-USB B |
| Zakres temperatur (eksploatacja): | 0 - 50 °C |
| Zakres wilgotności względnej: | 10 - 80 % |
| Skrócona instrukcja obsługi: | Tak |
| Przewodowa sieć LAN: | Tak |
| Kompatybilność 3D: | Tak |
| Zakres temperatur (przechowywanie): | -40 - 85 °C |
| Model: | Nadajnik AV |
| Maks. rozdzielczość: | 3840 x 2160 px |
| Maksymalna częstotliwość odświeżania: | 120 Hz |
| Wersja HDMI: | 2.0 |
| HDCP: | Tak |
| Szerokość pasma: | 18 Gbit/s |
| Możliwości montowania w stelażu: | Tak |
| Materiały: | Metal |
| Wersja USB: | 2.0 |
| Złącze światłowodowe: | LC |
| Maksymalny dystans transferu: | 2500 m |
| HDMI in: | 2 |
| Obsługiwane tryby wideo: | 1080p, 2160p |
| Głębia kolorów: | 36 bit |
| Wejścia RJ-45: | 2 |
| Wspierane długości fal: | 778,850,911,980 nm |
| Porty wejściowe RS-232: | 1 |
| Rozszerzone dane identyfikacyjne wyświetlacza (EDID): | Tak |
| Przejście RS-232: | Tak |
| Przedni panel kontrolny (TX): | Tak |
| Emulacja EDID (TX): | Tak |
| Pamięć EDID (TX): | Tak |
Potrzebujesz pomocy?
Jeśli potrzebujesz pomocy z Lightware HDMI20-OPTC-TX220-FOX, zadaj pytanie poniżej, a inni użytkownicy Ci odpowiedzą
Instrukcje przedłużacz AV Lightware

25 Września 2024

25 Września 2024

25 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024

9 Września 2024
Instrukcje przedłużacz AV
- przedłużacz AV Philips
- przedłużacz AV Gigabyte
- przedłużacz AV Roland
- przedłużacz AV KEF
- przedłużacz AV StarTech.com
- przedłużacz AV Crestron
- przedłużacz AV Nedis
- przedłużacz AV AG Neovo
- przedłużacz AV D-Link
- przedłużacz AV ATen
- przedłużacz AV Manhattan
- przedłużacz AV Tripp Lite
- przedłużacz AV Dynaudio
- przedłużacz AV Lindy
- przedłużacz AV LogiLink
- przedłużacz AV Digitus
- przedłużacz AV Oehlbach
- przedłużacz AV AVMATRIX
- przedłużacz AV Renkforce
- przedłużacz AV Adder
- przedłużacz AV DataVideo
- przedłużacz AV One For All
- przedłużacz AV Black Box
- przedłużacz AV Pyle
- przedłużacz AV Iogear
- przedłużacz AV Intellinet
- przedłużacz AV Vivotek
- przedłużacz AV Peerless-AV
- przedłużacz AV Audio Pro
- przedłużacz AV Kindermann
- przedłużacz AV Bogen
- przedłużacz AV Edimax
- przedłużacz AV Planet
- przedłużacz AV Blustream
- przedłużacz AV LevelOne
- przedłużacz AV Vivolink
- przedłużacz AV Teufel
- przedłużacz AV Vision
- przedłużacz AV Abus
- przedłużacz AV Rocstor
- przedłużacz AV Hama
- przedłużacz AV Marmitek
- przedłużacz AV Smart-AVI
- przedłużacz AV Schwaiger
- przedłużacz AV Micro Connect
- przedłużacz AV Allnet
- przedłużacz AV Marshall Electronics
- przedłużacz AV AJA
- przedłużacz AV Trevi
- przedłużacz AV Atlona
- przedłużacz AV Gefen
- przedłużacz AV SEADA
- przedłużacz AV Monacor
- przedłużacz AV I3-Technologies
- przedłużacz AV Alfatron
- przedłużacz AV Megasat
- przedłużacz AV Speaka
- przedłużacz AV Belkin
- przedłużacz AV SWIT
- przedłużacz AV Sescom
- przedłużacz AV Kramer
- przedłużacz AV KanexPro
- przedłużacz AV Kopul
- przedłużacz AV Analog Way
- przedłużacz AV Apantac
- przedłużacz AV AMX
- przedłużacz AV C2G
- przedłużacz AV Act
- przedłużacz AV Eminent
- przedłużacz AV Techly
- przedłużacz AV Matrox
- przedłużacz AV Steren
- przedłużacz AV InFocus
- przedłużacz AV Konig
- przedłużacz AV Dune
- przedłużacz AV Genexis
- przedłużacz AV Wentronic
- przedłużacz AV Peerless
- przedłużacz AV Monoprice
- przedłużacz AV WyreStorm
- przedłużacz AV TV One
- przedłużacz AV MIPRO
- przedłużacz AV Provision ISR
- przedłużacz AV UTEPO
- przedłużacz AV Aitech
- przedłużacz AV SIIG
- przedłużacz AV Polycom
- przedłużacz AV Advantech
- przedłużacz AV Intelix
- przedłużacz AV MuxLab
- przedłużacz AV Extron
- przedłużacz AV ASSMANN Electronic
- przedłużacz AV Avocent
- przedłużacz AV Comprehensive
- przedłużacz AV Rose
- przedłużacz AV Ebode
- przedłużacz AV Accell
- przedłużacz AV Ecler
- przedłużacz AV Rose Electronics
- przedłużacz AV Epcom
- przedłużacz AV CYP
- przedłużacz AV SmartAVI
- przedłużacz AV IMG Stage Line
- przedłużacz AV HELGI
- przedłużacz AV Liberty
- przedłużacz AV PureTools
- przedłużacz AV Enson
- przedłużacz AV Approx
- przedłużacz AV Hall Research
- przedłużacz AV Seco-Larm
- przedłużacz AV ConnectPro
- przedłużacz AV Kanex
- przedłużacz AV TechLogix Networx
- przedłużacz AV PureLink
- przedłużacz AV DVDO
- przedłużacz AV Camplex
Najnowsze instrukcje dla przedłużacz AV

8 Kwietnia 2025

1 Kwietnia 2025

1 Kwietnia 2025

1 Kwietnia 2025

1 Kwietnia 2025

1 Kwietnia 2025

26 Lutego 2025

20 Lutego 2025

20 Lutego 2025

7 Lutego 2025